Long-Term Liver Expression of an Apolipoprotein A-I Mimetic Peptide Attenuates Interferon-Alpha-Induced Inflammation and Promotes Antiviral Activity
- PMID: 33708194
- PMCID: PMC7940203
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.620283
Long-Term Liver Expression of an Apolipoprotein A-I Mimetic Peptide Attenuates Interferon-Alpha-Induced Inflammation and Promotes Antiviral Activity
Abstract
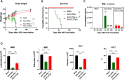
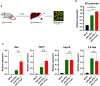
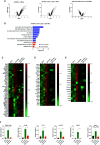
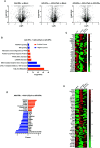
Apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptides are amphipathic alpha-helix peptides that display similar functions to apolipoprotein A-I. Preclinical and clinical studies have demonstrated the safety and efficacy of apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptides in multiple indications associated with inflammatory processes. In this study, we evaluated the effect of the long-term expression of L37pA in the liver by an adeno-associated virus (AAV-L37pA) on the expression of an adeno-associated virus encoding interferon-alpha (AAV-IFNα). Long-term IFNα expression in the liver leads to lethal hematological toxicity one month after AAV administration. Concomitant administration of AAV-L37pA prevented the lethal toxicity since the IFNα expression was reduced one month after AAV administration. To identify the mechanism of action of L37pA, a genomic and proteomic analysis was performed 15 days after AAV administration when a similar level of IFNα and interferon-stimulated genes were observed in mice treated with AAV-IFNα alone and in mice treated with AAV-IFNα and AAV-L37pA. The coexpression of the apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide L37pA with IFNα modulated the gene expression program of IFNα, inducing a significant reduction in inflammatory pathways affecting pathogen-associated molecular patterns receptor, dendritic cells, NK cells and Th1 immune response. The proteomic analysis confirmed the impact of the L37pA activity on several inflammatory pathways and indicated an activation of LXR/RXR and PPPARα/γ nuclear receptors. Thus, long-term expression of L37pA induces an anti-inflammatory effect in the liver that allows silencing of IFNα expression mediated by an adeno-associated virus.
Keywords: adeno-associated virus; antiviral; apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide; liver; type I Interferon.
Copyright © 2021 Fernandez-Sendin, Di Trani, Bella, Vasquez, Ardaiz, Gomar, Arrizabalaga, Ciordia, Corrales, Aranda and Berraondo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antitumor effect of an adeno-associated virus expressing apolipoprotein A-1 fused to interferon alpha in an interferon alpha-resistant murine tumor model.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 17;8(3):5247-5255. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14127. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28029653 Free PMC article.
-
Liver-directed gene therapy of chronic hepadnavirus infection using interferon alpha tethered to apolipoprotein A-I.J Hepatol. 2015 Aug;63(2):329-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.02.048. Epub 2015 Mar 12. J Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 25772035 Free PMC article.
-
Anchoring interferon alpha to apolipoprotein A-I reduces hematological toxicity while enhancing immunostimulatory properties.Hepatology. 2011 Jun;53(6):1864-73. doi: 10.1002/hep.24306. Epub 2011 May 2. Hepatology. 2011. PMID: 21425312
-
Immunity to adeno-associated virus vectors in animals and humans: a continued challenge.Gene Ther. 2008 Jun;15(11):808-16. doi: 10.1038/gt.2008.54. Epub 2008 Apr 3. Gene Ther. 2008. PMID: 18385765 Review.
-
Immune responses to AAV in clinical trials.Curr Gene Ther. 2007 Oct;7(5):316-24. doi: 10.2174/156652307782151425. Curr Gene Ther. 2007. PMID: 17979678 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of human tear proteome reveals differentially abundance proteins in thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy.PeerJ. 2022 Jul 12;10:e13701. doi: 10.7717/peerj.13701. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 35846879 Free PMC article.
-
The crucial regulatory role of type I interferon in inflammatory diseases.Cell Biosci. 2023 Dec 20;13(1):230. doi: 10.1186/s13578-023-01188-z. Cell Biosci. 2023. PMID: 38124132 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gomaraschi M, Calabresi L, Rossoni G, Iametti S, Franceschini G, Stonik JA, et al. . Anti-inflammatory and cardioprotective activities of synthetic high-density lipoprotein containing apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptides. J Pharmacol Exp Ther (2008) 324(2):776–83. 10.1124/jpet.107.129411 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

