Role of HCA2 in Regulating Intestinal Homeostasis and Suppressing Colon Carcinogenesis
- PMID: 33708203
- PMCID: PMC7940178
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.606384
Role of HCA2 in Regulating Intestinal Homeostasis and Suppressing Colon Carcinogenesis
Abstract
Hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 2 (HCA2) is vital for sensing intermediates of metabolism, including β-hydroxybutyrate and butyrate. It also regulates profound anti-inflammatory effects in various tissues, indicating that HCA2 may serve as an essential therapeutic target for mediating inflammation-associated diseases. Butyrate and niacin, endogenous and exogenous ligands of HCA2, have been reported to play an essential role in maintaining intestinal homeostasis. HCA2, predominantly expressed in diverse immune cells, is also present in intestinal epithelial cells (IECs), where it regulates the intricate communication network between diet, microbiota, and immune cells. This review summarizes the physiological role of HCA2 in intestinal homeostasis and its pathological role in intestinal inflammation and cancer.
Keywords: HCA2; anti-inflammatory; colon cancer; intestinal homeostasis; intestinal inflammation; microbiota; mucosal immunity.
Copyright © 2021 Li, McCafferty and Judd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
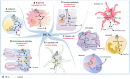
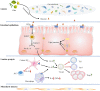
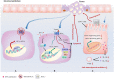
References
-
- Abedi V, Lu P, Hontecillas R, Verma M, Vess G, Philipson CW, et al. . Phase III placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial with synthetic Crohn's disease patients to evaluate treatment response. Computational Modeling-Based Discovery of Novel Classes of Anti-Inflammatory Drugs that Target Lanthionine Synthetase C-Like Protein. Emerg Trends Comput Biol Bioinform Syst Biol Syst Appl. (2015) 2:169. 10.1016/b978-0-12-804203-8.00028-6 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

