Phenotypic and Functional Characterization of Double Negative B Cells in the Blood of Individuals With Obesity
- PMID: 33708209
- PMCID: PMC7940530
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.616650
Phenotypic and Functional Characterization of Double Negative B Cells in the Blood of Individuals With Obesity
Abstract
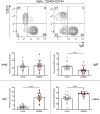
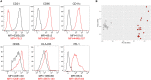
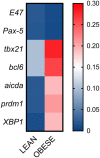
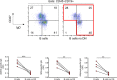
We have previously shown that obesity is associated with increased secretion of IgG antibodies with anti-self-reactivity. In this paper, we confirm and extend our previous findings. We show that the plasma of individuals with obesity is enriched in autoimmune antibodies whose levels are positively associated with blood frequencies of the subset of Double Negative (DN) B cells, which is the most pro-inflammatory B cell subset. We also show that DN B cells, significantly increased in the blood of obese versus lean individuals, are characterized by higher expression of immune activation markers and of the transcription factor T-bet, both associated with autoimmunity. The removal of DN B cells from the peripheral B cell pool significantly decreases in vitro secretion of anti-self IgG antibodies. These results altogether confirm the crucial role of DN B cells in the secretion of anti-self IgG antibodies in individuals with obesity.
Keywords: B cells; aging; antibody responses; inflammation; obesity.
Copyright © 2021 Frasca, Diaz, Romero and Blomberg.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

