Reactive Oxygen Species and Their Involvement in Red Blood Cell Damage in Chronic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 33708334
- PMCID: PMC7932781
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6639199
Reactive Oxygen Species and Their Involvement in Red Blood Cell Damage in Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
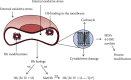
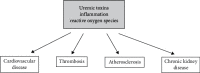
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) released in cells are signaling molecules but can also modify signaling proteins. Red blood cells perform a major role in maintaining the balance of the redox in the blood. The main cytosolic protein of RBC is hemoglobin (Hb), which accounts for 95-97%. Most other proteins are involved in protecting the blood cell from oxidative stress. Hemoglobin is a major factor in initiating oxidative stress within the erythrocyte. RBCs can also be damaged by exogenous oxidants. Hb autoxidation leads to the generation of a superoxide radical, of which the catalyzed or spontaneous dismutation produces hydrogen peroxide. Both oxidants induce hemichrome formation, heme degradation, and release of free iron which is a catalyst for free radical reactions. To maintain the redox balance, appropriate antioxidants are present in the cytosol, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and peroxiredoxin 2 (PRDX2), as well as low molecular weight antioxidants: glutathione, ascorbic acid, lipoic acid, α-tocopherol, β-carotene, and others. Redox imbalance leads to oxidative stress and may be associated with overproduction of ROS and/or insufficient capacity of the antioxidant system. Oxidative stress performs a key role in CKD as evidenced by the high level of markers associated with oxidative damage to proteins, lipids, and DNA in vivo. In addition to the overproduction of ROS, a reduced antioxidant capacity is observed, associated with a decrease in the activity of SOD, GPx, PRDX2, and low molecular weight antioxidants. In addition, hemodialysis is accompanied by oxidative stress in which low-biocompatibility dialysis membranes activate phagocytic cells, especially neutrophils and monocytes, leading to a respiratory burst. This review shows the production of ROS under normal conditions and CKD and its impact on disease progression. Oxidative damage to red blood cells (RBCs) in CKD and their contribution to cardiovascular disease are also discussed.
Copyright © 2021 Krzysztof Gwozdzinski et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets as a source of oxidative stress in chronic vascular diseases: detoxifying mechanisms and potential therapeutic options.Thromb Haemost. 2012 Sep;108(3):435-42. doi: 10.1160/TH12-04-0248. Epub 2012 Jul 26. Thromb Haemost. 2012. PMID: 22836558 Review.
-
Several lines of antioxidant defense against oxidative stress: antioxidant enzymes, nanomaterials with multiple enzyme-mimicking activities, and low-molecular-weight antioxidants.Arch Toxicol. 2024 May;98(5):1323-1367. doi: 10.1007/s00204-024-03696-4. Epub 2024 Mar 14. Arch Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38483584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Free radicals, metals and antioxidants in oxidative stress-induced cancer.Chem Biol Interact. 2006 Mar 10;160(1):1-40. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2005.12.009. Epub 2006 Jan 23. Chem Biol Interact. 2006. PMID: 16430879 Review.
-
Red blood cell oxidative stress impairs oxygen delivery and induces red blood cell aging.Front Physiol. 2014 Feb 28;5:84. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00084. eCollection 2014. Front Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24616707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Redox- and non-redox-metal-induced formation of free radicals and their role in human disease.Arch Toxicol. 2016 Jan;90(1):1-37. doi: 10.1007/s00204-015-1579-5. Epub 2015 Sep 7. Arch Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 26343967 Review.
Cited by
-
Stable Nitroxide as Diagnostic Tools for Monitoring of Oxidative Stress and Hypoalbuminemia in the Context of COVID-19.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 24;25(15):8045. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158045. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Initial Preoperative Hemoglobin Level Affects the Rate of Decline in Anti-Müllerian Hormone Levels after Laparoscopic Ovarian Cystectomy in Women with Ovarian Endometriosis.J Menopausal Med. 2023 Dec;29(3):127-133. doi: 10.6118/jmm.23024. J Menopausal Med. 2023. PMID: 38230596 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Cucurbiturils on the Production of Reactive Oxygen Species by T- and B-Lymphocytes, Platelets and Red Blood Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 11;24(2):1441. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021441. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674954 Free PMC article.
-
Red Blood Cell Metabolism In Vivo and In Vitro.Metabolites. 2023 Jun 27;13(7):793. doi: 10.3390/metabo13070793. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 37512500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Red blood cells as biomarkers and mediators in complications of diabetes mellitus: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Feb 23;103(8):e37265. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000037265. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38394525 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gastaldello K., Husson C., Wens R., Vanherweghem J. L., Tielemans C. Role of complement and platelet-activating factor in the stimulation of phagocytosis and reactive oxygen species production during haemodialysis. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation. 2000;15(10):1638–1646. doi: 10.1093/ndt/15.10.1638. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chelombitko M. A. Role of reactive oxygen species in inflammation: a minireview. Moscow University Biological Sciences Bulletin. 2018;73(4):199–202. doi: 10.3103/S009639251804003X. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

