Albumin Reduces Oxidative Stress and Neuronal Apoptosis via the ERK/Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway after Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Rats
- PMID: 33708336
- PMCID: PMC7932792
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/8891373
Albumin Reduces Oxidative Stress and Neuronal Apoptosis via the ERK/Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway after Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Rats
Abstract
Background: Albumin has been regarded as a potent antioxidant with free radical scavenging activities. Oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis are responsible for its highly damaging effects on brain injury after intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH). Here, the present study investigated the neuroprotective effect of albumin against early brain injury after ICH and the potential underlying mechanisms.
Methods: Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats were subjected to intrastriatal injection of autologous blood to induce ICH. Human serum albumin was given by intravenous injection 1 h after ICH. U0126, an inhibitor of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK1/2), and ML385, an inhibitor of nuclear factor-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), were intraperitoneally administered 1 h before ICH induction. Short- and long-term neurobehavioral tests, western blotting, immunofluorescence staining, oxidative stress evaluations, and apoptosis measurements were performed.
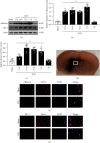
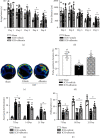
Results: Endogenous expression of albumin (peaked at 5 days) and heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1, peaked at 24 h) was increased after ICH compared with the sham group. Albumin and HO-1 were colocalized with neurons. Compared with vehicle, albumin treatment significantly improved short- and long-term neurobehavioral deficits and reduced oxidative stress and neuronal death at 72 h after ICH. Moreover, albumin treatment significantly promoted the phosphorylation of ERK1/2; increased the expression of Nrf2, HO-1, and Bcl-2; and downregulated the expression of Romo1 and Bax. U0126 and ML385 abolished the treatment effects of albumin on behavior and protein levels after ICH.
Conclusions: Albumin attenuated oxidative stress-related neuronal death may in part via the ERK/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway after ICH in rats. Our study suggests that albumin may be a novel therapeutic method to ameliorate brain injury after ICH.
Copyright © 2021 Shuixiang Deng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Activation of the Melanocortin-1 Receptor by NDP-MSH Attenuates Oxidative Stress and Neuronal Apoptosis through PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 Pathway after Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Mice.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Nov 12;2020:8864100. doi: 10.1155/2020/8864100. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 33274009 Free PMC article.
-
Heme oxygenase 1 plays role of neuron-protection by regulating Nrf2-ARE signaling post intracerebral hemorrhage.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Sep 1;8(9):10156-63. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26617723 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant CCL17 Enhances Hematoma Resolution and Activation of CCR4/ERK/Nrf2/CD163 Signaling Pathway After Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Mice.Neurotherapeutics. 2020 Oct;17(4):1940-1953. doi: 10.1007/s13311-020-00908-4. Neurotherapeutics. 2020. PMID: 32783091 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the Nrf2-Heme Oxygenase-1 Axis after Intracerebral Hemorrhage.Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(15):2226-2237. doi: 10.2174/1381612822666161027150616. Curr Pharm Des. 2017. PMID: 27799046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The SIRT-1/Nrf2/HO-1 axis: Guardians of neuronal health in neurological disorders.Behav Brain Res. 2025 Jan 5;476:115280. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2024.115280. Epub 2024 Oct 4. Behav Brain Res. 2025. PMID: 39368713 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging trends and hotspots of Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 in nervous system diseases.World J Clin Cases. 2023 Nov 16;11(32):7833-7851. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i32.7833. World J Clin Cases. 2023. PMID: 38073678 Free PMC article.
-
Association of high fibrinogen to albumin ratio with long-term mortality in patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage.Front Neurol. 2024 Jul 19;15:1412804. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1412804. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39099785 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of Fat Mass and Obesity-Related Gene-Mediated Heme Oxygenase-1 m6A Modification in the Recovery of Neurological Function in Mice with Spinal Cord Injury.Orthop Surg. 2024 May;16(5):1175-1186. doi: 10.1111/os.14002. Epub 2024 Mar 21. Orthop Surg. 2024. PMID: 38514911 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 as a potential therapeutic target in intracerebral hemorrhage.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Sep 29;15:995518. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.995518. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36245922 Free PMC article. Review.
-
P‑hydroxybenzyl alcohol ameliorates neuronal cerebral ischemia‑reperfusion injury by activating mitochondrial autophagy through SIRT1.Mol Med Rep. 2023 Mar;27(3):68. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2023.12955. Epub 2023 Feb 17. Mol Med Rep. 2023. PMID: 36799156 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

