Involvement of the Mediastinal Subpleural Pulmonary Parenchyma on Chest CT in COVID-19 patients: A Case Series
- PMID: 33708340
- PMCID: PMC7942959
- DOI: 10.3941/jrcr.v14i11.3974
Involvement of the Mediastinal Subpleural Pulmonary Parenchyma on Chest CT in COVID-19 patients: A Case Series
Abstract
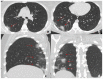
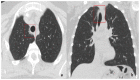
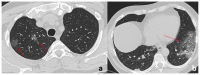
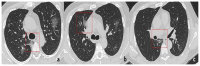
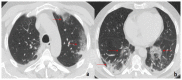
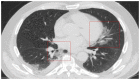
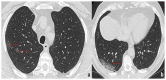
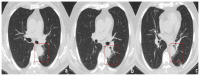
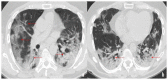
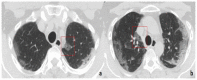
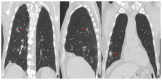
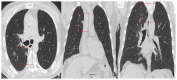
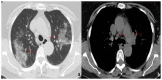
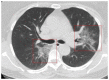
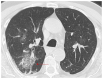
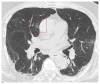
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is an infectious disease caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). First identified in December 2019 in Wuhan, China, it has since become a global pandemic. Although the reference standard for SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis is real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), computed tomography (CT) is recommended for both initial evaluation and follow-up. The CT findings in COVID-19 are varied, but typical ground-glass opacities are usually reported to occupy a peripheral costal subpleural distribution. Here we report eight confirmed COVID-19 cases who underwent clinical evaluation, laboratory testing, and unenhanced chest CT. In all patients, chest CT showed the presence of ground-glass opacities in the mediastinal subpleural parenchyma. While these cases also showed the typical CT features of COVID-19, involvement of the mediastinal subpleural parenchyma should not lower the index of suspicion for COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronavirus disease 2019; GGOs; chest CT; ground-glass opacities; lung consolidation; mediastinal pleura.
Copyright Journal of Radiology Case Reports.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Imaging and clinical features of patients with 2019 novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2020 May;47(5):1275-1280. doi: 10.1007/s00259-020-04735-9. Epub 2020 Feb 28. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32107577 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and radiological features of novel coronavirus pneumonia.J Xray Sci Technol. 2020;28(3):391-404. doi: 10.3233/XST-200687. J Xray Sci Technol. 2020. PMID: 32538893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early chest CT features of patients with 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19) pneumonia: relationship to diagnosis and prognosis.Eur Radiol. 2020 Nov;30(11):6178-6185. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-06978-4. Epub 2020 Jun 9. Eur Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32518987 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between Chest Computed Tomography and Lung Ultrasonography in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19).Ultrasound Med Biol. 2020 Nov;46(11):2918-2926. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2020.07.003. Epub 2020 Jul 13. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32771222 Free PMC article.
-
The novel coronavirus pneumonia (COVID-19): a pictorial review of chest CT features.Diagn Interv Radiol. 2021 Mar;27(2):188-194. doi: 10.5152/dir.2020.20304. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2021. PMID: 32815523 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) Pandemic. Geneva: World Health Organization; Oct 27, 2020. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous