Non-muscle myosin II knockdown improves survival and therapeutic effects of implanted bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury
- PMID: 33708889
- PMCID: PMC7940885
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-20-4851
Non-muscle myosin II knockdown improves survival and therapeutic effects of implanted bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury
Abstract
Background: Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) have been shown to have some beneficial effects in acute lung injury (ALI), but the therapeutic effects are limited due to apoptosis or necrosis after transplantation into injured lungs. Here, we aim to explore whether Non-muscle myosin II (NM-II) knockdown could enhance BMSCs survival and improve therapeutic effects in ALI.
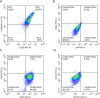
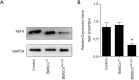
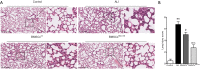
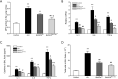
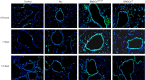
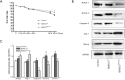
Methods: MSCs, isolated from rat bone marrow, were transfected with the small interfering RNA (siRNA) targeted to NM-II mRNA by a lentivirus vector. Rats were equally randomized to four groups: the control group was given normal saline via tail vein; the other three groups underwent intratracheal lipopolysaccharide (LPS) instillation followed by administration with either normal saline, BMSCs transduced with lentivirus-enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP) empty vector, or BMSCs transduced with lentivirus-eGFP NM-II siRNA. Hematoxylin and eosin staining was used to evaluate lung histopathologic changes and Masson trichrome staining was used to assess lung fibrosis. The myeloperoxidase activity was also tested in lung tissues. The mRNA expression of inflammatory cytokines in lung tissues was determined via quantitative reverse transcription PCR. Sex-determining region of the Y chromosome gene expression was measured by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) assay. The expression of self-renewal activity and apoptosis-associated proteins were measured by Western blot.
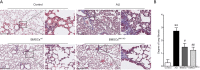
Results: Transplantation of NM-II siRNA-modified BMSCs could improve histopathological morphology, decrease inflammatory infiltrates, down-regulate the expression levels of inflammatory cytokines, and reduce pulmonary interstitial edema. NM-II siRNA-modified BMSCs showed antifibrotic properties and alleviated the degrees of pulmonary fibrosis induced by endotoxin. In addition, NM-II knockdown BMSCs showed slightly better therapeutic effect on lung inflammation when compared with control BMSCs. The beneficial effects of NM-II siRNA-modified BMSCs may be attributed to enhanced self-renewal activity and decreased apoptosis.
Conclusions: NM-II knockdown could inhibit the apoptosis of implanted BMSCs in lung tissues and improve its self-renewal activity. NM-II siRNA-modified BMSCs have a slightly enhanced ability to attenuate lung injury after LPS challenge.
Keywords: Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs); acute lung injury (ALI); gene therapy; non-muscle myosin II (NM-II).
2021 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/atm-20-4851). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Effects of non-muscle myosin Ⅱ silenced bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells transplantation on lung extracellular matrix in rats after endotoxin/lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury].Zhonghua Shao Shang Yu Chuang Mian Xiu Fu Za Zhi. 2022 May 20;38(5):422-433. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501225-20220212-00024. Zhonghua Shao Shang Yu Chuang Mian Xiu Fu Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35599418 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Lats2-Underexpressing Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorate LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice.Mediators Inflamm. 2019 Oct 21;2019:4851431. doi: 10.1155/2019/4851431. eCollection 2019. Mediators Inflamm. 2019. PMID: 31772503 Free PMC article.
-
A combination of ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction with transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promotes recovery of acute liver injury.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018 Dec 29;9(1):356. doi: 10.1186/s13287-018-1098-4. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 30594241 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cells Modified with Heme Oxygenase-1 Have Enhanced Paracrine Function and Attenuate Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory and Oxidative Damage in Pulmonary Microvascular Endothelial Cells.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;49(1):101-122. doi: 10.1159/000492847. Epub 2018 Aug 28. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30153667
-
The role of bone marrow-derived stem cells in lung regeneration and repair.2008 Sep 30. In: StemBook [Internet]. Cambridge (MA): Harvard Stem Cell Institute; 2008–. 2008 Sep 30. In: StemBook [Internet]. Cambridge (MA): Harvard Stem Cell Institute; 2008–. PMID: 20614615 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
[Effects of non-muscle myosin Ⅱ silenced bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells transplantation on lung extracellular matrix in rats after endotoxin/lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury].Zhonghua Shao Shang Yu Chuang Mian Xiu Fu Za Zhi. 2022 May 20;38(5):422-433. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501225-20220212-00024. Zhonghua Shao Shang Yu Chuang Mian Xiu Fu Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35599418 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Boosting therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in pulmonary fibrosis: The role of genetic modification and preconditioning strategies.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2023;26(9):1001-1015. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2023.69023.15049. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37605719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Effects and mechanism of annexin A1-overexpressing human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of mice with acute respiratory distress syndrome].Zhonghua Shao Shang Yu Chuang Mian Xiu Fu Za Zhi. 2023 May 20;39(5):456-464. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501225-20220408-00130. Zhonghua Shao Shang Yu Chuang Mian Xiu Fu Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37805755 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
The myosin II inhibitor, blebbistatin, ameliorates pulmonary endothelial barrier dysfunction in acute lung injury induced by LPS via NMMHC IIA/Wnt5a/β-catenin pathway.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 1;450:116132. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2022.116132. Epub 2022 Jun 15. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35716767 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of FoxM1 Enhanced the Protective Effect of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury through the Activation of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2023 Feb 11;2023:8324504. doi: 10.1155/2023/8324504. eCollection 2023. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2023. PMID: 36820407 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
