Regulation of smooth muscle contractility by the epithelium in rat tracheas: role of prostaglandin E2 induced by the neurotransmitter acetylcholine
- PMID: 33708940
- PMCID: PMC7944331
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-20-5500
Regulation of smooth muscle contractility by the epithelium in rat tracheas: role of prostaglandin E2 induced by the neurotransmitter acetylcholine
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have suggested the involvement of epithelium in modulating the contractility of neighboring smooth muscle cells. However, the mechanism underlying epithelium-derived relaxation in airways remains largely unclear. This study aimed to investigate the mechanism underlying epithelium-dependent smooth muscle relaxation mediated by neurotransmitters.
Methods: The contractile tension of Sprague-Dawley (SD) rat tracheal rings were measured using a mechanical recording system. Intracellular Ca2+ level was measured using a Ca2+ fluorescent probe Fluo-3 AM, and the fluorescence signal was recorded by a laser scanning confocal imaging system. The prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) content was measured using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit.
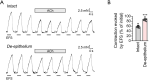
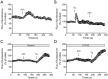
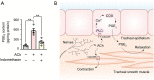
Results: We observed that the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh) restrained the electric field stimulation (EFS)-induced contraction in the intact but not epithelium-denuded rat tracheal rings. After inhibiting the muscarinic ACh receptor (mAChR) or cyclooxygenase (COX), a critical enzyme in prostaglandin synthesis, the relaxant effect of ACh was attenuated. Exogenous PGE2 showed a similar inhibitory effect on the EFS-evoked contraction of tracheal rings. Moreover, ACh triggered phospholipase C (PLC)-coupled Ca2+ release from intracellular Ca2+ stores and stimulated COX-dependent PGE2 production in primary cultured rat tracheal epithelial cells.
Conclusions: Collectively, this study demonstrated that ACh induced rat tracheal smooth muscle relaxation by promoting PGE2 release from tracheal epithelium, which might provide valuable insights into the cross-talk among neurons, epithelial cells and neighboring smooth muscle cells in airways.
Keywords: Cyclooxygenase (COX); neurotransmitter; prostaglandin E2 (PGE2); smooth muscle relaxation; tracheal epithelium.
2021 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/atm-20-5500). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

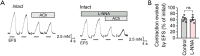

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
