Eriocitrin attenuates ischemia reperfusion-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in rats with acute kidney injury by regulating the dual-specificity phosphatase 14 (DUSP14)-mediated Nrf2 and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) pathways
- PMID: 33708977
- PMCID: PMC7944338
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-21-337
Eriocitrin attenuates ischemia reperfusion-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in rats with acute kidney injury by regulating the dual-specificity phosphatase 14 (DUSP14)-mediated Nrf2 and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) pathways
Abstract
Background: Ischemia reperfusion (IR)-induced acute kidney injury (AKI) is accompanied by increased inflammatory response and oxidative stress. Eriocitrin is a flavonoid that is mainly derived from lemon or citrate juice. It exhibits various pharmacological effects and is known to have antioxidant and anti-steatotic benefits. However, research on the effect of eriocitrin against IR-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in AKI is limited.
Methods: In this study, an OGD/R of HK-2 cell in vitro and rat model of AKI in vivo were constructed. Then the cell or rats were treated with eriocitrin at different doses (60, 30, 10 mg/kg). The levels of apoptotic were detected by flow cytometry. Inflammatory and oxidative stress factors in supernatant in vitro and tissue in vivo. Meanwhile, Western blot was used to detect the change of dual-specificity phosphatase 14 (DUSP14), Nrf2 and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB).
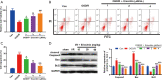
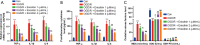
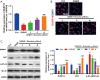
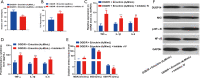
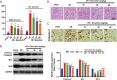
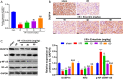
Results: Eriocitrin attenuated apoptosis of the human renal tubular epithelial cell line HK-2 mediated by oxygen glucose deprivation/reperfusion via the repression of inflammation and oxidative stress in a dose-dependent manner. Eriocitrin also enhanced the levels of dual-specificity phosphatase 14 (DUSP14) and Nrf2, and decreased NF-κB phosphorylation. Furthermore, the in vivo experiments indicated that eriocitrin dose-dependently alleviated IR-induced AKI and apoptosis in rats. By elevating DUSP14, eriocitrin promoted the expression of Nrf2 and inactivated NF-κB, thereby downregulating inflammation and oxidative stress. Moreover, inhibiting DUSP14 expression with protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) inhibitor IV reversed the kidney-protective effects of Eriocitrin.
Conclusions: Eriocitrin protected IR-induced AKI by attenuating oxidative stress and inflammation via elevating DUSP14, thereby providing a theoretical basis for the treatment of IR-induced AKI.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury (AKI); dual-specificity phosphatase 14 (DUSP14); eriocitrin; inflammation; oxidative stress.
2021 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/atm-21-337). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Machado-Aranda D, Suresh M, Yu B, et al. RNA From Necrotic Cells Drives the Acute Inflammatory Response and Injury Through Toll-Like Receptor-3 (TLR-3) Dependent Pathway in Lung Contusion. J Surg Res 2013;179:326. 10.1016/j.jss.2012.10.660 - DOI
-
- Wang L, Wang Q, Sheng K, et al. A new graphene nanocomposite modified electrode as efficient voltammetric sensor for determination of eriocitrin. J Electroanal Chem 2017;785:96-102. 10.1016/j.jelechem.2016.11.061 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
