Characterization of Partially Covered Self-Expandable Metallic Stents for Esophageal Cancer Treatment: In Vivo Degradation
- PMID: 33709689
- PMCID: PMC8045022
- DOI: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.0c01773
Characterization of Partially Covered Self-Expandable Metallic Stents for Esophageal Cancer Treatment: In Vivo Degradation
Abstract
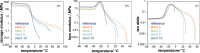
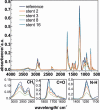
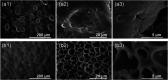
Partially covered self-expandable metallic esophageal stent (SEMS) placement is the most frequently applied palliative treatment in esophageal cancer. Structural characterization of explanted 16 nitinol-polyurethane SEMS (the group of 6 females, 10 males, age 40-80) was performed after their removal due to dysfunction. The adverse bulk changes in the polymer structure were identified using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), differential mechanical thermal analysis (DMTA), and attenuated total reflectance infrared spectroscopy (ATR-IR) and discussed in terms of melting point shift (9 °C), glass-transition shift (4 °C), differences in viscoelastic behavior, and systematic decrease of peaks intensities corresponding to C-H, C═O, and C-N polyurethane structural bonds. The scanning electron and confocal microscopic observations revealed all major types of surface degradation, i.e., surface cracks, peeling off of the polymer material, and surface etching. The changes in the hydrophobic polyurethane surfaces were also revealed by a significant decrease in wettability (74°) and the corresponding increase of the surface free energy (31 mJ/m2). To understand the in vivo degradation, the in vitro tests in simulated salivary and gastric fluids were performed, which mimic the environments of proximal and distal ends, respectively. It was concluded that the differences in the degradation of the proximal and distal ends of prostheses strongly depend on the physiological environment, in particular stomach content. Finally, the necessity of the in vivo tests for SEMS degradation is pointed out.
Keywords: biomaterial; esophageal cancer; esophageal stent; esophagus; in vivo degradation; polyurethane.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures









References
-
- Naghavi M.; Abajobir A. A.; Abbafati C.; Murray C. J. L.; et al. Global, regional, and national age-sex specifc mortality for 264 causes of death, 1980-2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017, 390, 1151–1210. 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32152-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Todua F.; Gagua R.; Maglakelidze M.; Maglakelidze D. Cancer incidence and mortality – Major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012, worldwide and Georgia. Bull. Georgian Natl. Acad. Sci. 2015, 9, 168–173.
-
- Yuan T.; Zheng R.; Yu J.; Edmonds L.; Wu W.; Cao J.; Gao F.; Zhu Y.; Cheng Y.; Cui W. Fabrication and evaluation of polymer-based esophageal stents for benign esophagus stricture insertion. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 16891–16898. 10.1039/C5RA23763G. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

