Perioperative Complications of Surgery for Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy: A Comparison Between 3 Procedures
- PMID: 33709809
- PMCID: PMC9972283
- DOI: 10.1177/2192568221998306
Perioperative Complications of Surgery for Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy: A Comparison Between 3 Procedures
Erratum in
-
Erratum to "Perioperative Complications of Surgery for Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy: A Comparison Between 3 Procedures".Global Spine J. 2023 Jan;13(1):257. doi: 10.1177/21925682221106197. Epub 2022 Jun 6. Global Spine J. 2023. PMID: 35666641 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Study design: Retrospective comparative study.
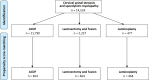
Objectives: To compare the perioperative complications of propensity score-matched cohorts of patients with degenerative cervical myelopathy (DCM), who were treated with anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF), posterior laminectomy with fusion, or laminoplasty.
Methods: The Humana PearlDiver Patient Record Database was queried using the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-9 and ICD-10) and the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes. Propensity score-matched analysis was done using multiple Chi-squared tests with Bonferroni correction of the significance level.
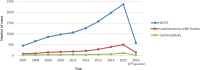
Results: Cohorts of 11,790 patients who had ACDF, 2,257 patients who had posterior laminectomy with fusion, and 477 patients who had laminoplasty, were identified. After propensity score matching, all the 3 groups included 464 patients. The incidence of dysphagia increased significantly following ACDF compared to laminoplasty, P < 0.001, and in laminectomy with fusion compared to laminoplasty, P < 0.001. The incidence of new-onset cervicalgia was higher in ACDF compared to laminoplasty, P = 0.005, and in laminectomy with fusion compared to laminoplasty, P = 0.004. The incidence of limb paralysis increased significantly in laminectomy with fusion compared to ACDF, P = 0.002. The revision rate at 1 year increased significantly in laminectomy with fusion compared to laminoplasty, P < 0.001, and in ACDF compared to laminoplasty, P < 0.001.
Conclusions: The incidence of dysphagia following laminectomy with fusion was not different compared to ACDF. Postoperative new-onset cervicalgia and revisions were least common in laminoplasty. The highest rate of postoperative limb paralysis was noticed in laminectomy with fusion.
Keywords: ACDF; cervical spinal stenosis; degenerative cervical myelopathy; laminectomy and fusion; laminoplasty; propensity score matching.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources