Hemoadsorption eliminates remdesivir from the circulation: Implications for the treatment of COVID-19
- PMID: 33710753
- PMCID: PMC7953359
- DOI: 10.1002/prp2.743
Hemoadsorption eliminates remdesivir from the circulation: Implications for the treatment of COVID-19
Abstract
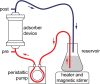
Both antiviral treatment with remdesivir and hemoadsorption using a CytoSorb® adsorption device are applied in the treatment of severe COVID-19. The CytoSorb® adsorber consists of porous polymer beads that adsorb a broad range of molecules, including cytokines but also several therapeutic drugs. In this study, we evaluated whether remdesivir and its main active metabolite GS-441524 would be adsorbed by CytoSorb® . Serum containing remdesivir or GS-441524 was circulated in a custom-made system containing a CytoSorb® device. Concentrations of remdesivir and GS-441524 before and after the adsorber were analyzed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Measurements of remdesivir in the outgoing tube after the adsorber indicated almost complete removal of remdesivir by the device. In the reservoir, concentration of remdesivir showed an exponential decay and was not longer detectable after 60 mins. GS-441524 showed a similar exponential decay but, unlike remdesivir, it reached an adsorption-desorption equilibrium at ~48 µg/L. Remdesivir and its main active metabolite GS-441524 are rapidly eliminated from the perfusate by the CytoSorb® adsorber device in vitro. This should be considered in patients for whom both therapies are indicated, and simultaneous application should be avoided. In general, plasma levels of therapeutic drugs should be closely monitored under concurrent CytoSorb® therapy.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; cytokine; hemoadsorption; remdesivir.
© 2021 The Authors. Pharmacology Research & Perspectives published by British Pharmacological Society and American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Paul Biever and Alexander Supady received speakers' honoraria from CytoSorbents, the manufacturer of the CytoSorb® device. The Department of Cardiology and Angiology I received a research grant from CytoSorbents not related to the present study.
Figures

References
-
- National Institutes of Health COVID‐19 Treatment Guidelines Panel. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID‐19) Treatment Guidelines. https://files.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/guidelines/section/sect.... Accessed January 19, 2021. - PubMed
-
- Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines on the Treatment and Management of Patients with COVID‐19. https://www.idsociety.org/globalassets/idsa/practice‐guidelines/covid‐19.... Accessed January 19, 2021. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Poli EC, Rimmele T, Schneider AG. Hemoadsorption with CytoSorb® . Intensive Care Med. 2019;45(2):236‐239. - PubMed
-
- United States Food and Drug Administration: CytoSorb® Emergency Use Authorization for Use in Patients with COVID‐19 Infection. https://www.fda.gov/media/136866/download. Accessed January 19, 2021.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

