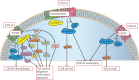
The biological role of the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 33710803
- PMCID: PMC8185864
- DOI: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2020.0140
The biological role of the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Esophageal cancer is the eighth most common malignant tumor and the sixth leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is the main histological type of esophageal cancer, and accounts for 90% of all cancer cases. Despite the progress made in surgery, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy, the mortality rate from esophageal cancer remains high, and the overall 5-year survival rate is less than 20%, even in developed countries. The C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12 (CXCL12) is a member of the CXC chemokine subgroup, which is widely expressed in a variety of tissues and cells. CXCL12 participates in the regulation of many physiological and pathological processes by binding to its specific receptor, C-X-C motif chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4), where it causes embryonic development, immune response, and angiogenesis. In addition, increasing evidence indicates that the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis plays an important role in the biological processes of tumor cells. Studies have shown that CXCL12 and its receptor, CXCR4, are highly expressed in ESCC. This abnormal expression contributes to tumor proliferation, lymph node and distant metastases, and worsening prognosis. At present, antagonists and imaging agents against CXCL12 or CXCR4 have been developed to interfere with the malignant process and monitor metastasis of tumors. This article summarizes the structure, function, and regulatory mechanism of CXCL12/CXCR4 and its role in the malignancy of ESCC. Current results from preclinical research targeting CXCL12/CXCR4 are also summarized to provide a reference for the clinical diagnosis and treatment of ESCC.
Keywords: C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12; CXC chemokine receptor 4; Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; antagonists; imaging agent.
Copyright © 2021 Cancer Biology & Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest are disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Chemokine CXCL12 Activates CXC Receptor 4 Metastasis Signaling Through the Upregulation of a CXCL12/CXCR4/MDMX (MDM4) Axis.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Dec 16;16(24):4194. doi: 10.3390/cancers16244194. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39766093 Free PMC article.
-
CXC chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) blockade in cancer treatment.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Aug;149(10):7945-7968. doi: 10.1007/s00432-022-04444-w. Epub 2023 Mar 11. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36905421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
Cited by
-
The role of miR-145-5p in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tumor-associated macrophages and selection of immunochemotherapy.J Thorac Dis. 2022 Jul;14(7):2493-2510. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-294. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 35928615 Free PMC article.
-
CXCR4 promotes the growth and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma as a critical downstream mediator of HIF-1α.Cancer Sci. 2022 Mar;113(3):926-939. doi: 10.1111/cas.15265. Epub 2022 Jan 17. Cancer Sci. 2022. PMID: 34990040 Free PMC article.
-
Recent progress in molecular mechanisms of postoperative recurrence and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Dec 14;28(46):6433-6477. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i46.6433. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36569275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemokines and their receptors in the esophageal carcinoma tumor microenvironment: key factors for metastasis and progression.Front Oncol. 2025 Mar 11;15:1523751. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1523751. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40134607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PSD3, regulated by PKM2, endows growth and metastasis advantages in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by modulating EMT progression.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):23212. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05649-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40603347 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ohashi S, Miyamoto S, Kikuchi O, Goto T, Amanuma Y, Muto M. Recent advances from basic and clinical studies of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2015;149:1700–15. - PubMed
-
- Ilson DH, van Hillegersberg R. Management of patients with adenocarcinoma or squamous cancer of the esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2018;154:437–51. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69:7–34. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources