Analysis of the HNF4A isoform-regulated transcriptome identifies CCL15 as a downstream target in gastric carcinogenesis
- PMID: 33710810
- PMCID: PMC8185874
- DOI: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2020.0131
Analysis of the HNF4A isoform-regulated transcriptome identifies CCL15 as a downstream target in gastric carcinogenesis
Abstract
Objective: Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α (HNF4A) has been demonstrated to be an oncogene in gastric cancer (GC). However, the roles of different HNF4A isoforms derived from the 2 different promoters (P1 and P2) and the underlying mechanisms remain obscure.
Methods: The expression and prognostic values of P1- and P2-HNF4A were evaluated in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) databases and GC tissues. Then, functional assays of P1- and P2-HNF4A were conducted both in vivo and in vitro. High-throughput RNA-seq was employed to profile downstream pathways in P1- and P2-HNF4A-overexpressing GC cells. The expression and gene regulation network of the candidate target genes identified by RNA-seq were characterized based on data mining and functional assays.
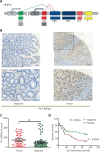
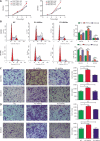
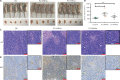
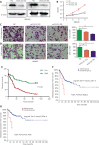
Results: HNF4A amplification was a key characteristic of GC in TCGA databases, especially for the intestinal type and early stage. Moreover, P1-HNF4A expression was significantly higher in tumor tissues than in adjacent non-tumor tissues (P < 0.05), but no significant differences were found in P2-HNF4A expression (P > 0.05). High P1-HNF4A expression indicated poor prognoses in GC patients (P < 0.01). Furthermore, P1-HNF4A overexpression significantly promoted SGC7901 and BGC823 cell proliferation, invasion and migration in vitro (P < 0.01). Murine xenograft experiments showed that P1-HNF4A overexpression promoted tumor growth (P < 0.05). Mechanistically, RNA-seq showed that the cytokine-cytokine receptor interactions pathway was mostly enriched in P1-HNF4A-overexpressing GC cells. Finally, chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 15 was identified as a direct target of P1-HNF4A in GC tissues.
Conclusions: P1-HNF4A was the main oncogene during GC progression. The cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction pathway played a pivotal role and may be a promising therapeutic target.
Keywords: CCL15; Gastric cancer; HNF4A; carcinogenesis; transcriptomics.
Copyright © 2021 Cancer Biology & Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest are disclosed.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Stratifying IVF population endometria using a prognosis gradient independent of endometrial timing†.Hum Reprod. 2025 Aug 12:deaf156. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deaf156. Online ahead of print. Hum Reprod. 2025. PMID: 40796355
-
A novel copper-induced cell death-related lncRNA prognostic signature associated with immune infiltration and clinical value in gastric cancer.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Sep;149(12):10543-10559. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-04916-7. Epub 2023 Jun 8. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37291405 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
Physical interventions to interrupt or reduce the spread of respiratory viruses.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jan 30;1(1):CD006207. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006207.pub6. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36715243 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
FOXP2 regulates thyroid cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis via transcriptional activation of RPS6KA6.Exp Ther Med. 2022 Jun;23(6):434. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11361. Epub 2022 May 9. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 35607372 Free PMC article.
-
GATA binding protein 5-mediated transcriptional activation of transmembrane protein 100 suppresses cell proliferation, migration and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer DU145 cells.Bioengineered. 2022 Apr;13(4):7972-7983. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2018979. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35358005 Free PMC article.
-
HNF4A-Bridging the Gap Between Intestinal Metaplasia and Gastric Cancer.Evol Bioinform Online. 2024 Apr 25;20:11769343241249017. doi: 10.1177/11769343241249017. eCollection 2024. Evol Bioinform Online. 2024. PMID: 38680615 Free PMC article.
-
Stress Reactivity, Susceptibility to Hypertension, and Differential Expression of Genes in Hypertensive Compared to Normotensive Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 4;23(5):2835. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052835. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269977 Free PMC article.
-
The role of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α (HNF4α) in tumorigenesis.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 28;12:1011230. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1011230. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36249028 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Chia NY, Deng N, Das K, Huang D, Hu L, Zhu Y, et al. Regulatory crosstalk between lineage-survival oncogenes KLF5, GATA4 and GATA6 cooperatively promotes gastric cancer development. Gut. 2015;64:707–19. - PubMed
-
- Xu C, Ooi WF, Qamra A, Tan J, Chua BY, Ho S, et al. HNF4alpha pathway mapping identifies wild-type IDH1 as a targetable metabolic node in gastric cancer. Gut. 2020;69:231–42. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
