A possible mechanism for neurofilament slowing down in myelinated axon: Phosphorylation-induced variation of NF kinetics
- PMID: 33711034
- PMCID: PMC7954336
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247656
A possible mechanism for neurofilament slowing down in myelinated axon: Phosphorylation-induced variation of NF kinetics
Abstract
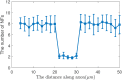
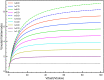
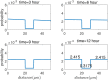
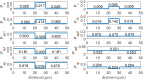
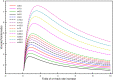
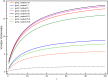
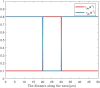
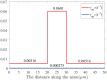
Neurofilaments(NFs) are the most abundant intermediate filaments that make up the inner volume of axon, with possible phosphorylation on their side arms, and their slow axonal transport by molecular motors along microtubule tracks in a "stop-and-go" manner with rapid, intermittent and bidirectional motion. The kinetics of NFs and morphology of axon are dramatically different between myelinate internode and unmyelinated node of Ranvier. The NFs in the node transport as 7.6 times faster as in the internode, and the distribution of NFs population in the internode is 7.6 folds as much as in the node of Ranvier. We hypothesize that the phosphorylation of NFs could reduce the on-track rate and slow down their transport velocity in the internode. By modifying the '6-state' model with (a) an extra phosphorylation kinetics to each six state and (b) construction a new '8-state' model in which NFs at off-track can be phosphorylated and have smaller on-track rate, our model and simulation demonstrate that the phosphorylation-induced decrease of on-track rate could slow down the NFs average velocity and increase the axonal caliber. The degree of phosphorylation may indicate the extent of velocity reduction. The Continuity equation used in our paper predicts that the ratio of NFs population is inverse proportional to the ratios of average velocity of NFs between node of Ranvier and internode. We speculate that the myelination of axon could increase the level of phosphorylation of NF side arms, and decrease the possibility of NFs to get on-track of microtubules, therefore slow down their transport velocity. In summary, our work provides a potential mechanism for understanding the phosphorylation kinetics of NFs in regulating their transport and morphology of axon in myelinated axons, and the different kinetics of NFs between node and internode.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Brown A. Slow axonal transport. Encyclopedia of Neuroscience. 2009; Vol 9: 1–9.
-
- De Waegh S, Lee M-Y, and Brady ST. Local modulation of neurofilament phosphorylation, axonal caliber, and slow axonal transport by myelinating Schwann cells. Cell. 1992; Vol 68: 451–463. - PubMed
-
- Hoffman PN. The synthesis, axonal transport and phosphorylation of neurofilaments determine axonal caliber in myelinated nerve fibers. The Neuroscientist. 1995; Vol 1(76): 76–83.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

