A systematic review of clinical and laboratory parameters associated with increased severity among COVID-19 patients
- PMID: 33711574
- PMCID: PMC7896120
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dsx.2021.02.020
A systematic review of clinical and laboratory parameters associated with increased severity among COVID-19 patients
Abstract
Background and aims: Corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has been an extremely difficult pandemic to contain and it has affected more than 148 countries worldwide. The main aim of this systematic review is to provide a comprehensive summary of clinical and laboratory parameters that are associated with and indicative of increased severity among COVID-19 patients.
Material and methods: All the available data from high-quality research articles relevant to the epidemiology, demographics, trends in hospitalization and outcomes, clinical signs and symptoms, diagnostic methods and treatment methods of COVID-19 were retrieved and evaluated for inclusion.
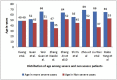
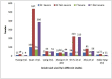
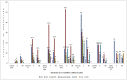
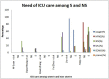
Results: As per our review, the mean age of patients in the severe group was 59.3 years compared to 46.5 years in non severe group. COVID-19 was more severe among men than women. Clinical presentation was variable among different studies. and dyspnea was the factor indicating severe disease. Laboratory parameters associated with increased severity were lymphopenia <0.8 × 109/L, thrombocytopenia 100 × 109/L, leucocytosis TC > 11 × 109/L, procalcitonin >0.5 ng/mL, d dimer >2 mcg/mL, aspartate transaminase elevation >150U/L, LDH >250U/L.
Conclusion: This systematic review suggests that COVID-19 is a disease with varied clinical presentation and laboratory parameters. The commonest clinical symptoms were fever, cough and dyspnea. The laboratory parameters associated with severe disease were lymphopenia, elevated LDH, D dimer and Procalcitonin.
Keywords: COVID-19; Clinical symptoms; Laboratory parameters; Systematic review.
Copyright © 2021 Diabetes India. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest There is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) situation report-72. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2... Published April 1st , 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

