Retrospective analysis of dermal absorption triple pack data
- PMID: 33712859
- PMCID: PMC12508965
- DOI: 10.14573/altex.2101121
Retrospective analysis of dermal absorption triple pack data
Abstract
Dermal toxicity is driven by the ability of a substance to penetrate the skin. The “triple pack” approach, which combines in vivo rat, in vitro rat, and in vitro human data, is used to calculate an estimated human dermal absorption factor (DAF). To assess the feasibility of deriving a DAF using only in vitro data, we retrospectively evaluated agrochemical formulations to compare the DAF derived from each individual method to the DAF generated from the triple pack approach. For most of the formulations evaluated, the in vitro rat method generated a similar or higher DAF value than the in vivo method. Absorption through in vitro human skin was similar to or less than that observed in rat skin for all formulations. For most of the formulations, the human in vitro method provided a similar or higher estimate of dermal absorption than the triple pack approach. For human health risk assessment, in vitro assays using human skin would be preferable, as they would be directly relevant to the species of interest and avoid overestimation of dermal absorption using rat models. However, rat in vitro studies would still have utility in the absence of human in vitro data. In vitro rat data provide estimates of dermal absorption that are at least as protective as in vivo rat data and thus could also be considered adequate for use in establishing DAFs. The comparisons presented support potentially using in vitro data alone for DAF derivation for human health risk assessment of pesticides.
Keywords: agrochemicals testing; in vitro; skin absorption.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
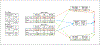

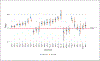

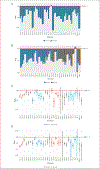


References
-
- EPA (1998). Health Effects Test Guidelines: OCSPP 870.7600 – Dermal Penetration (No. EPA 712-C-98–350). Washington, D.C., U.S. Environmental ProtectionAgency. https://regulations.gov/document?D=EPA-HQ-OPPT-2009-0156-0048
-
- NAFTA (2008). Dermal Absorption Group Position Paper on Use of In Vitro Dermal Absorption Data in Risk Assessment. North American Free Trade Agreement Dermal Absorption Working Group. Pp. 1–3. Unpublished; available upon request.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

