The impact of regionalized trauma care on the distribution of severely injured patients in the Netherlands
- PMID: 33712892
- PMCID: PMC9001217
- DOI: 10.1007/s00068-021-01615-1
The impact of regionalized trauma care on the distribution of severely injured patients in the Netherlands
Abstract
Background: Twenty years ago, an inclusive trauma system was implemented in the Netherlands. The goal of this study was to evaluate the impact of structured trauma care on the concentration of severely injured patients over time.
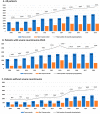
Methods: All severely injured patients (Injury Severity Score [ISS] ≥ 16) documented in the Dutch Trauma Registry (DTR) in the calendar period 2008-2018 were included for analysis. We compared severely injured patients, with and without severe neurotrauma, directly brought to trauma centers (TC) and non-trauma centers (NTC). The proportion of patients being directly transported to a trauma center was determined, as was the total Abbreviated Injury Score (AIS), and ISS.
Results: The documented number of severely injured patients increased from 2350 in 2008 to 4694 in 2018. During this period, on average, 70% of these patients were directly admitted to a TC (range 63-74%). Patients without severe neurotrauma had a lower chance of being brought to a TC compared to those with severe neurotrauma. Patients directly presented to a TC were more severely injured, reflected by a higher total AIS and ISS, than those directly transported to a NTC.
Conclusion: Since the introduction of a well-organized trauma system in the Netherlands, trauma care has become progressively centralized, with more severely injured patients being directly presented to a TC. However, still 30% of these patients is initially brought to a NTC. Future research should focus on improving pre-hospital triage to facilitate swift transfer of the right patient to the right hospital.
Keywords: Regionalization of care; The Netherlands; Trauma care; Trauma system.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures




References
-
- Goris RJADJ. De zorg voor detrauma-patiënt: meer en beter onderzoek nodig. Medisch Contact. 1984;39:301–302.
-
- Ministerie van Volksgezondheid Welzijn en Sport. Met Zorg Verbonden. 1997.
-
- Nederlandse Vereniging voorTraumatologie. Traumazorg; onze zorg. 1997.
-
- American College of Surgeons- Committee on Trauma. Resources for optimal care of the injured patients. American College of Surgeons,; Chicago, 19981999.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

