Granzyme B PET Imaging of Combined Chemotherapy and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy in Colon Cancer
- PMID: 33713000
- PMCID: PMC8410722
- DOI: 10.1007/s11307-021-01596-y
Granzyme B PET Imaging of Combined Chemotherapy and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy in Colon Cancer
Abstract
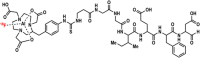
Purpose: Chemotherapeutic adjuvants, such as oxaliplatin (OXA) and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), that enhance the immune system, are being assessed as strategies to improve durable response rates when used in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) monotherapy in cancer patients. In this study, we explored granzyme B (GZB), released by tumor-associated immune cells, as a PET imaging-based stratification marker for successful combination therapy using a fluorine-18 (18F)-labelled GZB peptide ([18F]AlF-mNOTA-GZP).
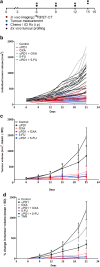
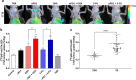
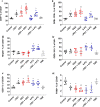
Methods: Using the immunocompetent CT26 syngeneic mouse model of colon cancer, we assessed the potential for [18F]AlF-mNOTA-GZP to stratify OXA/5-FU and ICI combination therapy response via GZB PET. In vivo tumor uptake of [18F]AlF-mNOTA-GZP in different treatment arms was quantified by PET, and linked to differences in tumor-associated immune cell populations defined by using multicolour flow cytometry.
Results: [18F]AlF-mNOTA-GZP tumor uptake was able to clearly differentiate treatment responders from non-responders when stratified based on changes in tumor volume. Furthermore, [18F]AlF-mNOTA-GZP showed positive associations with changes in tumor-associated lymphocytes expressing GZB, namely GZB+ CD8+ T cells and GZB+ NK+ cells.
Conclusions: [18F]AlF-mNOTA-GZP tumor uptake, driven by changes in immune cell populations expressing GZB, is able to stratify tumor response to chemotherapeutics combined with ICIs. Our results show that, while the immunomodulatory mode of action of the chemotherapies may be different, the ultimate mechanism of tumor lysis through release of Granzyme B is an accurate biomarker for treatment response.
Keywords: Checkpoint inhibitors; Chemotherapy; Granzyme B; Lymphocytes; Tumor.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Granzyme B PET Imaging Stratifies Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Response in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Mol Imaging. 2021 Dec 9;2021:9305277. doi: 10.1155/2021/9305277. eCollection 2021. Mol Imaging. 2021. PMID: 35936114 Free PMC article.
-
Granzyme B PET Imaging of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Combinations in Colon Cancer Phenotypes.Mol Imaging Biol. 2020 Oct;22(5):1392-1402. doi: 10.1007/s11307-020-01519-3. Mol Imaging Biol. 2020. PMID: 32705455 Free PMC article.
-
Granzyme B PET Imaging in Response to In Situ Vaccine Therapy Combined with αPD1 in a Murine Colon Cancer Model.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jan 8;14(1):150. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14010150. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35057046 Free PMC article.
-
The role of PET molecular imaging in immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in lung cancer: Precision medicine and visual monitoring.Eur J Radiol. 2022 Apr;149:110200. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2022.110200. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Eur J Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35158214 Review.
-
Molecular imaging biomarkers for immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy.Theranostics. 2020 Jan 1;10(4):1708-1718. doi: 10.7150/thno.38339. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32042331 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Imaging Kv1.3 Expressing Memory T Cells as a Marker of Immunotherapy Response.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Feb 26;14(5):1217. doi: 10.3390/cancers14051217. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35267526 Free PMC article.
-
Granzyme B PET Imaging Stratifies Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Response in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Mol Imaging. 2021 Dec 9;2021:9305277. doi: 10.1155/2021/9305277. eCollection 2021. Mol Imaging. 2021. PMID: 35936114 Free PMC article.
-
Colon Cancer Diagnosis Based on Machine Learning and Deep Learning: Modalities and Analysis Techniques.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Nov 28;22(23):9250. doi: 10.3390/s22239250. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36501951 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Serine Proteases at the Tumor-Stroma Interface.Front Immunol. 2022 Feb 11;13:832418. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.832418. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35222418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular imaging to support cancer immunotherapy.J Immunother Cancer. 2022 Aug;10(8):e004949. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-004949. J Immunother Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35922089 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

