Ribosome states signal RNA quality control
- PMID: 33713598
- PMCID: PMC8041214
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.02.022
Ribosome states signal RNA quality control
Abstract
Eukaryotic cells integrate multiple quality control (QC) responses during protein synthesis in the cytoplasm. These QC responses are signaled by slow or stalled elongating ribosomes. Depending on the nature of the delay, the signal may lead to translational repression, messenger RNA decay, ribosome rescue, and/or nascent protein degradation. Here, we discuss how the structure and composition of an elongating ribosome in a troubled state determine the downstream quality control pathway(s) that ensue. We highlight the intersecting pathways involved in RNA decay and the crosstalk that occurs between RNA decay and ribosome rescue.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests R.G. is a member of the scientific advisory board at the journal Molecular Cell.
Figures
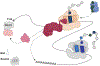
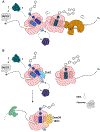
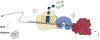
References
-
- Andersen DS and Leevers SJ (2007) ‘The essential drosophila ATP-binding cassette domain protein, pixie, binds the 40 S ribosome in an ATP-dependent manner and is required for translation initiation’, Journal of Biological Chemistry, 282(20), pp. 14752–14760. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M701361200. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barthelme D, Dinkelaker S, Albers S-V, Londei P, Ermler U and Tampé R (2011) ‘Ribosome recycling depends on a mechanistic link between the FeS cluster domain and a conformational switch of the twin-ATPase ABCE1.’, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 108(8), pp. 3228–33. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1015953108. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

