Time-resolved systems immunology reveals a late juncture linked to fatal COVID-19
- PMID: 33713619
- PMCID: PMC7874909
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.018
Time-resolved systems immunology reveals a late juncture linked to fatal COVID-19
Abstract
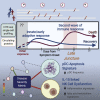
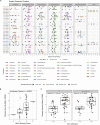
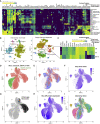
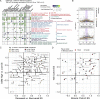
COVID-19 exhibits extensive patient-to-patient heterogeneity. To link immune response variation to disease severity and outcome over time, we longitudinally assessed circulating proteins as well as 188 surface protein markers, transcriptome, and T cell receptor sequence simultaneously in single peripheral immune cells from COVID-19 patients. Conditional-independence network analysis revealed primary correlates of disease severity, including gene expression signatures of apoptosis in plasmacytoid dendritic cells and attenuated inflammation but increased fatty acid metabolism in CD56dimCD16hi NK cells linked positively to circulating interleukin (IL)-15. CD8+ T cell activation was apparent without signs of exhaustion. Although cellular inflammation was depressed in severe patients early after hospitalization, it became elevated by days 17-23 post symptom onset, suggestive of a late wave of inflammatory responses. Furthermore, circulating protein trajectories at this time were divergent between and predictive of recovery versus fatal outcomes. Our findings stress the importance of timing in the analysis, clinical monitoring, and therapeutic intervention of COVID-19.
Keywords: CITE-seq; COVID-19; exhaustion; immune juncture; mixed-effect statistical modeling; single cell multi-omics; time-resolved.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures










References
-
- Bastard P., Rosen L.B., Zhang Q., Michailidis E., Hoffmann H.-H., Zhang Y., Dorgham K., Philippot Q., Rosain J., Béziat V., et al. HGID Lab. NIAID-USUHS Immune Response to COVID Group. COVID Clinicians. COVID-STORM Clinicians. Imagine COVID Group. French COVID Cohort Study Group. Milieu Intérieur Consortium. CoV-Contact Cohort. Amsterdam UMC Covid-19 Biobank. COVID Human Genetic Effort Autoantibodies against type I IFNs in patients with life-threatening COVID-19. Science. 2020;370:eabd4585. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bates D., Mächler M., Bolker B., Walker S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015;67:1–48.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

