Coinfection of tuberculosis and COVID-19 limits the ability to in vitro respond to SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 33713816
- PMCID: PMC7944764
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2021.02.090
Coinfection of tuberculosis and COVID-19 limits the ability to in vitro respond to SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
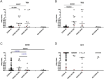
Objectives: The interaction of COVID-19 and tuberculosis (TB) are still poor characterized. Here we evaluated the immune response specific for Micobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) and SARS-CoV-2 using a whole-blood-based assay-platform in COVID-19 patients either with TB or latent TB infection (LTBI).
Methods: We evaluated IFN-γ level in plasma from whole-blood stimulated with Mtb antigens in the Quantiferon-Plus format or with peptides derived from SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, Wuhan-Hu-1 isolate (CD4-S).
Results: We consecutively enrolled 63 COVID-19, 10 TB-COVID-19 and 11 LTBI-COVID-19 patients. IFN-γ response to Mtb-antigens was significantly associated to TB status and therefore it was higher in TB-COVID-19 and LTBI-COVID-19 patients compared to COVID-19 patients (p ≤ 0.0007). Positive responses against CD4-S were found in 35/63 COVID-19 patients, 7/11 LTBI-COVID-19 and only 2/10 TB-COVID-19 patients. Interestingly, the responders in the TB-COVID-19 group were less compared to COVID-19 and LTBI-COVID-19 groups (p = 0.037 and 0.044, respectively). Moreover, TB-COVID-19 patients showed the lowest quantitative IFN-γ response to CD4-S compared to COVID-19-patients (p = 0.0336) and LTBI-COVID-19 patients (p = 0.0178).
Conclusions: Our data demonstrate that COVID-19 patients either TB or LTBI have a low ability to build an immune response to SARS-CoV-2 while retaining the ability to respond to Mtb-specific antigens.
Keywords: COVID-19; Co-infection; IFN-gamma response; M. tuberculosis; Tuberculosis; Whole blood assay.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Cantini F., Nannini C., Niccoli L., Petrone L., Ippolito G., Goletti D. Risk of tuberculosis reactivation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and psoriatic arthritis receiving non-anti-TNF-targeted biologics. Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:8909834. doi: 10.1155/2017/8909834. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Durrheim D.N., Crowcroft N.S., Strebel P.M. Measles — the epidemiology of elimination. Vaccine. 2014;32:6880–6883. S0264-410X(14)01451-0. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

