Metabolic regulation of tissue-resident memory CD8+ T cells
- PMID: 33714873
- PMCID: PMC8164981
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coph.2021.02.004
Metabolic regulation of tissue-resident memory CD8+ T cells
Abstract
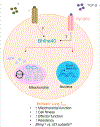
Intracellular metabolic adaptations help define the function and homeostasis of memory CD8+ T cells. These cells, which promote protection against infections or cancer, undergo consecutive metabolic shifts, ultimately relying on mitochondrial-related pathways. Past CD8+ T cell metabolism studies focused on circulating memory cells, which are exclusive to secondary lymphoid organs or recirculate between lymphoid and non-lymphoid organs. Yet, now there is unequivocal evidence that memory CD8+ T cells reside in many non-lymphoid organs and mediate protective immunity in barrier tissues. The metabolic adaptations occurring in forming and established tissue-resident memory CD8+ T cells are currently subject of intense research. In this review, we discuss the latest breakthroughs on the transcriptional and protein control of tissue-resident memory CD8+ T cell metabolism.
Keywords: Bhlhe40; Memory CD8(+) T cells; Memory precursor; Mitochondria; P2RX7; T(RM) cells.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement
Nothing declared.
Figures

References
-
- Farber DL, Netea MG, Radbruch A, Rajewsky K, Zinkernagel RM: Immunological memory: lessons from the past and a look to the future. Nat Rev Immunol 2016, 16:124–128. - PubMed
-
- Williams MA, Bevan MJ: Effector and memory CTL differentiation. Annu Rev Immunol 2007, 25:171–192. - PubMed
-
- Speiser DE, Utzschneider DT, Oberle SG, Munz C, Romero P, Zehn D: T cell differentiation in chronic infection and cancer: functional adaptation or exhaustion? Nat Rev Immunol 2014, 14:768–774. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

