The multi-kinase inhibitor TG02 induces apoptosis and blocks B-cell receptor signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia through dual mechanisms of action
- PMID: 33714981
- PMCID: PMC7956145
- DOI: 10.1038/s41408-021-00436-0
The multi-kinase inhibitor TG02 induces apoptosis and blocks B-cell receptor signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia through dual mechanisms of action
Abstract
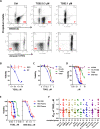
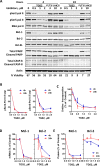
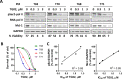
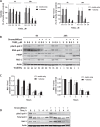
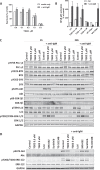
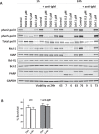
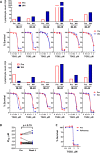
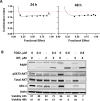
The constitutive activation of B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling, together with the overexpression of the Bcl-2 family anti-apoptotic proteins, represents two hallmarks of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) that drive leukemia cell proliferation and sustain their survival. TG02 is a small molecule multi-kinase inhibitor that simultaneously targets both of these facets of CLL pathogenesis. First, its inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 9 blocked the activation of RNA polymerase II and transcription. This led to the depletion of Mcl-1 and rapid induction of apoptosis in the primary CLL cells. This mechanism of apoptosis was independent of CLL prognostic factors or prior treatment history, but dependent on the expression of BAX and BAK. Second, TG02, which inhibits the members of the BCR signaling pathway such as Lck and Fyn, blocked BCR-crosslinking-induced activation of NF-κB and Akt, indicating abrogation of BCR signaling. Finally, the combination of TG02 and ibrutinib demonstrated moderate synergy, suggesting a future combination of TG02 with ibrutinib, or use in patients that are refractory to the BCR antagonists. Thus, the dual inhibitory activity on both the CLL survival pathway and BCR signaling identifies TG02 as a unique compound for clinical development in CLL and possibly other B cell malignancies.
Conflict of interest statement
F.J.B. was employed by Tragara Pharmaceuticals. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

