Surging trends in prescriptions and costs of antidepressants in England amid COVID-19
- PMID: 33715138
- PMCID: PMC7955799
- DOI: 10.1007/s40199-021-00390-z
Surging trends in prescriptions and costs of antidepressants in England amid COVID-19
Abstract
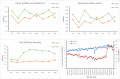
The social restrictions amid coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic have posed a serious threat to mental health and have implications in the use of medications for mental health including antidepressants (ADs). This study investigated the trends in prescriptions and costs of various ADs in England during COVID-19 pandemic. National prescribing rates and net ingredient costs (NIC) of all ADs prescriptions during 2016 to 2020 were analyed. The total number of ADs prescriptions dispensed during COVID-19 pandemic (January to December 2020) were 78 million, 4 million more than in 2019 that costed NHS England £ 139 million more than in 2019. Sertraline, an SSRI antidepressant drug, alone accounted for an extra £113 million during 2020 than in 2019. The peak dispensing for ADs was observed in March 2020 while the total costs for AD drugs peaked in April 2020. The rising prescription costs for ADs during COVID-19 pandemic is a potential cause of concern, in particular the increasing use in adolescents and younger adults needs attention, who are at a higher risk of life-threatening adverse drug reactions.
Keywords: Antidepressants; Anxiety; Cost; Depression; Interventions; Mental health; Prescribing trends; SARS-CoV-2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mental Health Foundation. 2020. Loneliness during coronavirus. https://www.mentalhealth.org.uk/coronavirus/coping-with-loneliness. Accessed 27 August 2020.
-
- Coronavirus and depression in adults, Great Britain: June 2020, 2020. Office for National Statistics. https://www.ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulationandcommunity/wellbeing/articles/c.... Accessed 28 August 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous