Relationship between de novo lipogenesis and serum sex hormone binding globulin in humans
- PMID: 33715205
- PMCID: PMC8287427
- DOI: 10.1111/cen.14459
Relationship between de novo lipogenesis and serum sex hormone binding globulin in humans
Abstract
Objective: Obesity and liver fat are associated with decreased levels of serum sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG). Laboratory studies suggest that hepatic de novo lipogenesis (DNL) is involved in the downregulation of SHBG synthesis. The aim of the present study was to address the role of DNL on serum SHBG in humans.
Design: A cross-sectional study examining the association between DNL, measured by stable isotopes, and serum SHBG, stratified by sex.
Participants: Healthy men (n = 34) and women (n = 21) were combined from two cross-sectional studies. Forty-two per cent of participants had hepatic steatosis, and the majority were overweight (62%) or obese (27%).
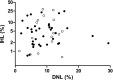
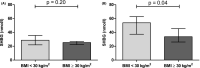
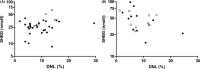
Results: DNL was inversely associated with SHBG in women (β: -0.015, 95% CI: -0.030; 0.000), but not in men (β: 0.007, 95% CI: -0.005; 0.019) (p for interaction = .068). Adjustment for study population, age and body mass index did not materially change these results, although statistical significance was lost after adjustment for serum insulin.
Conclusions: An inverse association between DNL and SHBG may explain the decreased SHBG levels that are observed in obesity, at least in women.
Keywords: de novo lipogenesis; liver fat; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; polycystic ovary syndrome; sex hormone binding globulin; stable isotopes.
© 2021 The Authors. Clinical Endocrinology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Williams EP, Mesidor M, Winters K, Dubbert PM, Wyatt SB. Overweight and obesity: prevalence, consequences, and causes of a growing public health problem. Curr Obes Rep. 2015;4(3):363‐370. - PubMed
-
- Shanbhogue VV, Mitchell DM, Rosen CJ, Bouxsein ML. Type 2 diabetes and the skeleton: new insights into sweet bones. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016;4(2):159‐173. - PubMed
-
- Telgenkamp I, Kusters YHAM, Schalkwijk CG, et al. Contribution of liver fat to weight loss‐induced changes in serum hepatokines: a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019;104(7):2719‐2727. - PubMed
-
- Hammond GL, Wu TS, Simard M. Evolving utility of sex hormone‐binding globulin measurements in clinical medicine. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2012;19(3):183‐189. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

