Lipid rafts as signaling hubs in cancer cell survival/death and invasion: implications in tumor progression and therapy: Thematic Review Series: Biology of Lipid Rafts
- PMID: 33715811
- PMCID: PMC7193951
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.TR119000439
Lipid rafts as signaling hubs in cancer cell survival/death and invasion: implications in tumor progression and therapy: Thematic Review Series: Biology of Lipid Rafts
Abstract
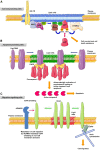
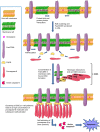
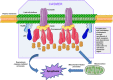
Cholesterol/sphingolipid-rich membrane domains, known as lipid rafts or membrane rafts, play a critical role in the compartmentalization of signaling pathways. Physical segregation of proteins in lipid rafts may modulate the accessibility of proteins to regulatory or effector molecules. Thus, lipid rafts serve as sorting platforms and hubs for signal transduction proteins. Cancer cells contain higher levels of intracellular cholesterol and lipid rafts than their normal non-tumorigenic counterparts. Many signal transduction processes involved in cancer development (insulin-like growth factor system and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-AKT) and metastasis [cluster of differentiation (CD)44] are dependent on or modulated by lipid rafts. Additional proteins playing an important role in several malignant cancers (e.g., transmembrane glycoprotein mucin 1) are also being detected in association with lipid rafts, suggesting a major role of lipid rafts in tumor progression. Conversely, lipid rafts also serve as scaffolds for the recruitment and clustering of Fas/CD95 death receptors and downstream signaling molecules leading to cell death-promoting raft platforms. The partition of death receptors and downstream signaling molecules in aggregated lipid rafts has led to the formation of the so-called cluster of apoptotic signaling molecule-enriched rafts, or CASMER, which leads to apoptosis amplification and can be pharmacologically modulated. These death-promoting rafts can be viewed as a linchpin from which apoptotic signals are launched. In this review, we discuss the involvement of lipid rafts in major signaling processes in cancer cells, including cell survival, cell death, and metastasis, and we consider the potential of lipid raft modulation as a promising target in cancer therapy.
Keywords: cholesterol • cholesterol-rich membrane domains • IGF system • PI3K/AKT signaling • Fas/CD95 • death receptor • CASMER • raft targeting.
Copyright © 2020 Copyright © 2020 Mollinedo and Gajate. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Lipid raft involvement in signal transduction in cancer cell survival, cell death and metastasis.Cell Prolif. 2022 Jan;55(1):e13167. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13167. Epub 2021 Dec 22. Cell Prolif. 2022. PMID: 34939255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid rafts as major platforms for signaling regulation in cancer.Adv Biol Regul. 2015 Jan;57:130-46. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2014.10.003. Epub 2014 Oct 27. Adv Biol Regul. 2015. PMID: 25465296 Review.
-
Clusters of apoptotic signaling molecule-enriched rafts, CASMERs: membrane platforms for protein assembly in Fas/CD95 signaling and targets in cancer therapy.Biochem Soc Trans. 2022 Jun 30;50(3):1105-1118. doi: 10.1042/BST20211115. Biochem Soc Trans. 2022. PMID: 35587168 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid raft-mediated Fas/CD95 apoptotic signaling in leukemic cells and normal leukocytes and therapeutic implications.J Leukoc Biol. 2015 Nov;98(5):739-59. doi: 10.1189/jlb.2MR0215-055R. Epub 2015 Aug 5. J Leukoc Biol. 2015. PMID: 26246489 Review.
-
Lipid rafts and Fas/CD95 signaling in cancer chemotherapy.Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2011 Sep;6(3):274-83. doi: 10.2174/157489211796957766. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2011. PMID: 21762074 Review.
Cited by
-
Alteration of cholesterol distribution at the plasma membrane of cancer cells: From evidence to pathophysiological implication and promising therapy strategy.Front Physiol. 2022 Nov 9;13:999883. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.999883. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36439249 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid rafts, caveolae, and epidermal growth factor receptor family: friends or foes?Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Oct 11;22(1):489. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01876-4. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39394159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid raft involvement in signal transduction in cancer cell survival, cell death and metastasis.Cell Prolif. 2022 Jan;55(1):e13167. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13167. Epub 2021 Dec 22. Cell Prolif. 2022. PMID: 34939255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aurora A and AKT Kinase Signaling Associated with Primary Cilia.Cells. 2021 Dec 20;10(12):3602. doi: 10.3390/cells10123602. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34944109 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SQLE promotes pancreatic cancer growth by attenuating ER stress and activating lipid rafts-regulated Src/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Aug 4;14(8):497. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05987-7. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 37542052 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Swinnen J. V., Brusselmans K., and Verhoeven G.. 2006. Increased lipogenesis in cancer cells: new players, novel targets. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care. 9: 358–365. - PubMed
-
- Chapman D. 1975. Phase transitions and fluidity characteristics of lipids and cell membranes. Q. Rev. Biophys. 8: 185–235. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

