Modelling the long-run learning impact of the Covid-19 learning shock: Actions to (more than) mitigate loss
- PMID: 33716394
- PMCID: PMC7923185
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijedudev.2020.102326
Modelling the long-run learning impact of the Covid-19 learning shock: Actions to (more than) mitigate loss
Abstract
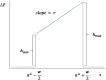
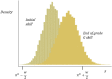
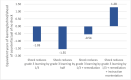
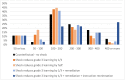
This paper uses a calibrated "pedagogical production function" model to estimate the potential long-term losses to children's learning from the temporary shock of Covid-19 related school closures. It then models possible gains from two mitigation strategies. Without mitigation, children could lose more than a full year's worth of learning from a three-month school closure because they will be behind the curriculum when they re-enter school and will fall further behind as time goes on. Remediation when children return to school reduces the long-term learning loss by half, but still leaves children more than half a year behind where they would have been with no shock. Remediation combined with long-term reorientation of curriculum to align with children's learning levels fully mitigates the long-term learning loss due to the shock and surpasses the learning in the counterfactual of no shock by more than a full year's worth of learning. Systems need to begin planning now for remediation programmes, and as they do so they should build programmes and train teachers in ways that can continue to produce benefits beyond the period immediately following reopening.
Keywords: Covid-19; International education; Learning loss; Remediation.
© 2020 The Author.
Figures

References
-
- Al-Samarrai S. World Bank; 2020. The Impact of the Covid-19 Pandemic on Education Financing.http://pubdocs.worldbank.org/en/734541589314089887/Covid-and-Ed-Finance-...
-
- Andrabi T., Daniels B., Das J. 2020. Human Capital Accumulation and Disasters: Evidence From the Pakistan Earthquake of 2005. RISE Working Paper Series. 20/039. - DOI
-
- Atuhurra J., Alinda V. 2017. Basic Education Curriculum Effectiveness Analysis in East Africa: Using the ‘Surveys of Enacted Curriculum’ Framework to Describe Primary Mathematics and English Content in Uganda. MPRA. Paper No. 79017.
-
- Beatty A., Pritchett L. Slow down, you’re going too fast: matching curricula to student skill levels. Int. J. Educ. Dev. 2015;40:276–288.
-
- Beatty A., et al. 2018. Indonesia Got Schooled: 15 Years of Rising Enrolment and Flat Learning Profiles. RISE Working Paper Series. 18/026. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
