Gregariousness, foraging effort, and affiliative interactions in lactating bonobos and chimpanzees
- PMID: 33716569
- PMCID: PMC7937187
- DOI: 10.1093/beheco/araa130
Gregariousness, foraging effort, and affiliative interactions in lactating bonobos and chimpanzees
Abstract
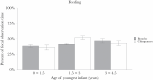
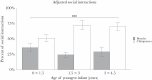
Fission-fusion dynamics have evolved in a broad range of animal taxa and are thought to allow individuals to mitigate feeding competition. While this is the principal benefit of fission-fusion, few studies have evaluated its costs. We compared gregariousness, foraging budgets, and social budgets between lactating bonobos and chimpanzees from wild populations to evaluate potential costs. Both species exhibit fission-fusion dynamics, but chimpanzees, particularly in East African populations, appear to experience higher feeding competition than bonobos. We expected lactating chimpanzees to be less gregarious than lactating bonobos; reduced gregariousness should allow lactating chimpanzees to mitigate the costs of higher feeding competition without requiring more foraging effort. However, we expected the reduced gregariousness of lactating chimpanzees to limit their time available for affiliative interactions. Using long-term data from LuiKotale bonobos and Gombe chimpanzees, we found that lactating chimpanzees were indeed less gregarious than lactating bonobos, while feeding and travel time did not differ between species. Contrary to our predictions, lactating females did not differ in social interaction time, and lactating chimpanzees spent proportionately more time interacting with individuals other than their immature offspring. Our results indicate that lactating chimpanzees can maintain social budgets comparable to lactating bonobos despite reduced gregariousness and without incurring additional foraging costs. We discuss potential explanations for why lactating bonobos are more gregarious.
Keywords: bonobos; chimpanzees; feeding competition; fission–fusion; predation risk; sociality.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the International Society for Behavioral Ecology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures



References
-
- Anestis SF. 2004. Female genito-genital rubbing in a group of captive chimpanzees. Int J Primatol. 25:477–488.
-
- Aureli F, Schaffner CM, Boesch C, Bearder SK, Call J, Chapman CA, Connor R, Fiore AD, Dunbar RIM, Henzi SP, et al. 2008. Fission‐fusion dynamics. Curr Anthropol. 49:627–654.
-
- Bădescu I, Katzenberg MA, Watts DP, Sellen DW. 2017. A novel fecal stable isotope approach to determine the timing of age-related feeding transitions in wild infant chimpanzees. Am J Phys Anthropol. 162:285–299. - PubMed
-
- Barclay RMR. 1989. The effect of reproductive condition on the foraging behavior of female hoary bats, Lasiurus cinereus. Behav Ecol Sociobiol. 24:31–37.
-
- Beauchamp G. 2012. Foraging speed in staging flocks of semipalmated sandpipers: evidence for scramble competition. Oecologia. 169:975–980. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

