Social Exclusion, Self-Forgiveness, Mindfulness, and Internet Addiction in College Students: a Moderated Mediation Approach
- PMID: 33716585
- PMCID: PMC7939101
- DOI: 10.1007/s11469-021-00506-1
Social Exclusion, Self-Forgiveness, Mindfulness, and Internet Addiction in College Students: a Moderated Mediation Approach
Abstract
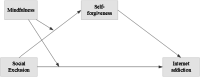
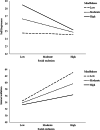
Internet addiction is a growingly prevalent behavioral addiction that causes numerous psychosocial problems. Investigating the causes and consequences of Internet addiction is fundamental to comprehend and prevent it. Therefore, the current study provided protective and promotive factors for undesired effects of social exclusion on Internet addiction. The study examined a moderated mediation model to test whether mindfulness moderated the mediating role of self-forgiveness in the association between social exclusion and Internet addiction among young adults. The participants of the present study included 358 undergraduate students attending a state university in Turkey. They ranged in age from 20 to 28 years (M = 21.89, SD = 1.95). The participants comprised 206 (57.5%) female and 152 (42.5%) male college young adults. Overall, the study findings indicated that self-forgiveness mediated the relationship between social exclusion and Internet addiction, and mindfulness moderated the mediating role of self-forgiveness in this association. Contending with negative outcomes of social exclusion and Internet addiction, and mitigating and buffering roles of self-forgiveness and mindfulness provide important implications to design prevention and intervention services for reducing Internet-related addictive behaviors.
Keywords: College students; Forgiveness; Internet addiction; Mindfulness; Social exclusion.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of InterestThe authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
References
-
- Akdeniz, S., & Deniz, M. (2016). Merhamet Ölçeği’nin Türkçeye uyarlanması: Geçerlik ve güvenirlik çalışması. The Journal of Happiness & Well-Being, 4(1), 50–61.
-
- Arslan G. Relationship between sense of rejection, academic achievement, academic efficacy, and educational purpose in high school students. Education and Science. 2016;41(183):293–304.
-
- Arslan G. Psychological maltreatment, forgiveness, mindfulness, and Internet addiction among young adults: A study of mediation effect. Computers in Human Behavior. 2017;72:57–66. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2017.02.037. - DOI
-
- Arslan G. School-based social exclusion, affective wellbeing, and mental health problems in adolescents: A study of mediator and moderator role of academic self-regulation. Child Indicators Research. 2018;11(3):963–980. doi: 10.1007/s12187-017-9486-3. - DOI
-
- Arslan G. Social exclusion, social support and psychological wellbeing at school: A study of mediation and moderation effect. Child Indicators Research. 2018;11(3):897–918. doi: 10.1007/s12187-017-9451-1. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources