Co-cultivation of diazotrophic terrestrial cyanobacteria and Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 33716612
- PMCID: PMC7923583
- DOI: 10.1002/elsc.202000068
Co-cultivation of diazotrophic terrestrial cyanobacteria and Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
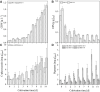
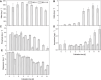
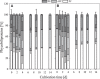
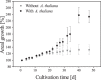
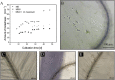
Diazotrophic cyanobacteria are able to fix N2 from the atmosphere and release it as bioavailable nitrogen what other organisms can utilize. Thus, they could be used as living nitrogen supplier whereby the use of fertilizer could be reduced in agricultural industry what results in a decrease of laughing gas released during fertilizer production. The diazotroph cyanobacterium Desmonostoc muscorum (D. muscorum) was characterized in shake flasks cultivated in nitrogen-free and nitrogen-containing medium. Similar growth rates were reached in both cultivations and the release of ammonium by D. muscorum was detected under nitrogen depletion. Subsequently, D. muscorum was co-cultivated with Arabidopsis thaliana (A. thaliana) in nitrogen-free medium. Additionally, the plant was cultivated in nitrogen containing and nitrogen-free medium without D. muscorum as reference. A co-cultivation led to higher growth rates of the cyanobacterium and similar growth of A. thaliana with similar maximum photochemical efficiency of photosystem II compared to the growth of nitrogen containing medium. Further, accumulation of cyanobacterial cells around the roots of A. thaliana was detected, indicating a successfully induced artificial symbiosis. Based on these results, D. muscorum could be a promising cyanobacterium as living nitrogen supplier for plants.
Keywords: co‐cultivation; cyanobacteria; diazotrophic biofilms; phototrophic biofilms; plants.
© 2020 The Authors. Engineering in Life Sciences published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Beneficial Effects of Cyanobacterial Co-Culture on Plant Growth.Life (Basel). 2022 Jan 31;12(2):223. doi: 10.3390/life12020223. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35207509 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Co-cultures from Plants and Cyanobacteria: A New Way for Production Systems in Agriculture and Bioprocess Engineering.Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2024;188:83-117. doi: 10.1007/10_2023_247. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38286901 Review.
-
Cyanobacteria-Derived Proline Increases Stress Tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana Root Hairs by Suppressing Programmed Cell Death.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Dec 14;11:490075. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.490075. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 33381127 Free PMC article.
-
[The accumulation and degradation dynamics of cyanophycin in cyanobacteria grown in symbiotic associations with plant tissues and cells].Mikrobiologiia. 2003 May-Jun;72(3):361-9. Mikrobiologiia. 2003. PMID: 12901011 Russian.
-
Isolation, growth, and nitrogen fixation rates of the Hemiaulus-Richelia (diatom-cyanobacterium) symbiosis in culture.PeerJ. 2020 Oct 8;8:e10115. doi: 10.7717/peerj.10115. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 33083143 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Process Technologies of Cyanobacteria.Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2023;183:303-352. doi: 10.1007/10_2022_214. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36571615
-
Insights into the Development of Phototrophic Biofilms in a Bioreactor by a Combination of X-ray Microtomography and Optical Coherence Tomography.Microorganisms. 2021 Aug 16;9(8):1743. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9081743. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34442822 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the Impact of Hexavalent Chromium (Cr VI) at Varied Concentrations on Spirulina platensis for Growth, Metal Sorption, and Photosynthetic Responses.Curr Microbiol. 2024 Jun 19;81(8):231. doi: 10.1007/s00284-024-03743-4. Curr Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38896297
References
-
- Stewart, W. M. , Dibb, D. W. , Johnston, A. E. , Smyth, T. J. , The contribution of commercial fertilizer nutrients to food production. Agron. J. 2005, 97, 1–6.
-
- Bates, D. R. , Hays, P. B., Atmospheric nitrous oxide. Planet. Space Sci. 1967, 15, 189–197.
-
- Singh, H. B. , Salas, L. J. , Shigeishi, H. , The distribution of nitrous oxide (N2O) in the global atmosphere and the Pacific Ocean. Tellus 1979, 31, 313–320.
-
- Rai, A. N. , Singh, A. K. , Syiem, M. B . Plant Growth‐Promoting Abilities in Cyanobacteria. Cyanobacteria. Cyanobacteria: Elsevier: 2019. 10.1016/B978-0-12-814667-5.00023-4. - DOI
-
- Rana, A. , Kabi, S. R. , Verma, S. , Adak, A. et al., Prospecting plant growth promoting bacteria and cyanobacteria as options for enrichment of macro‐ and micronutrients in grains in ricewheat cropping sequence. Cogent Food & Agric. 2015, 1, 1477.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
