Implementation of QbD strategies in the inoculum expansion of a mAb production process
- PMID: 33716618
- PMCID: PMC7923587
- DOI: 10.1002/elsc.202000056
Implementation of QbD strategies in the inoculum expansion of a mAb production process
Abstract
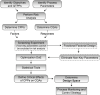
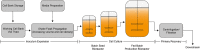
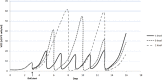
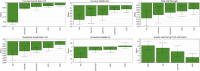
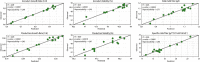
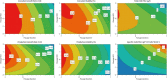
The quality by design approach was introduced to the biopharmaceutical industry over 15 years ago. This principle is widely implemented in the characterization of monoclonal antibody production processes. Anyway, the early process phase, namely the inoculum expansion, was not yet investigated and characterized for most processes. In order to increase the understanding of early process parameter interactions and their influence on the later production process, a risk assessment followed by a design of experiments approach was conducted. The DoE included the critical parameters methotrexate (MTX) concentration, initial passage viable cell density and passage duration. Multivariate data analysis led to mathematical regression models and the establishment of a designated design space for the studied parameters. It was found that the passage duration as well as the initial viable cell density for each passage during the inoculum expansion have severe effects on the growth rate and viability of the early process phase. Furthermore, the variations during the inoculum expansion directly influenced the production process responses. This carry-over of factor effects highlights the crucial impact of early process failures and the importance of process analysis and control during the first part of mAb production processes.
Keywords: CHO; PAT; QbD; inoculum expansion; mAb.
© 2020 The Authors. Engineering in Life Sciences published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
We confirm that all corresponding authors agree with the submission and publication of this paper and that there is no conflict of interest concerning financial and personal relationships. The manuscript does not contain neither experiments using animals nor human studies. Furthermore, we confirm that the article has not been published previously by any of the authors and is not under consideration for publication elsewhere at the time of submission.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Employing QbD strategies to assess the impact of cell viability and density on the primary recovery of monoclonal antibodies.Eng Life Sci. 2022 Dec 23;23(2):e202200056. doi: 10.1002/elsc.202200056. eCollection 2023 Feb. Eng Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 36751474 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of a mAb production process with regard to robustness and product quality using quality by design principles.Eng Life Sci. 2022 Jun 3;22(7):484-494. doi: 10.1002/elsc.202100172. eCollection 2022 Jul. Eng Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35865649 Free PMC article.
-
QbD-guided pharmaceutical development of Pembrolizumab biosimilar candidate PSG-024 propelled to industry meeting primary requirements of comparability to Keytruda®.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2022 Jun 1;173:106171. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2022.106171. Epub 2022 Apr 1. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2022. PMID: 35378209
-
Product Development, Manufacturing, and Packaging of Solid Dosage Forms Under QbD and PAT Paradigm: DOE Case Studies for Industrial Applications.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2019 Sep 16;20(8):313. doi: 10.1208/s12249-019-1515-8. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2019. PMID: 31529232 Review.
-
Towards the implementation of quality by design to the production of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies with desired glycosylation patterns.Biotechnol Prog. 2010 Nov-Dec;26(6):1505-27. doi: 10.1002/btpr.470. Biotechnol Prog. 2010. PMID: 20665659 Review.
Cited by
-
A Novel 3D-Printed and Miniaturized Periodic Counter Current Chromatography System for Continuous Purification of Monoclonal Antibodies.Micromachines (Basel). 2024 Mar 13;15(3):382. doi: 10.3390/mi15030382. Micromachines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38542629 Free PMC article.
-
Machine Learning-Powered Optimization of a CHO Cell Cultivation Process.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2025 May;122(5):1153-1164. doi: 10.1002/bit.28943. Epub 2025 Jan 31. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2025. PMID: 39887676 Free PMC article.
-
Employing QbD strategies to assess the impact of cell viability and density on the primary recovery of monoclonal antibodies.Eng Life Sci. 2022 Dec 23;23(2):e202200056. doi: 10.1002/elsc.202200056. eCollection 2023 Feb. Eng Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 36751474 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of a mAb production process with regard to robustness and product quality using quality by design principles.Eng Life Sci. 2022 Jun 3;22(7):484-494. doi: 10.1002/elsc.202100172. eCollection 2022 Jul. Eng Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35865649 Free PMC article.
-
Upstream cell culture process characterization and in-process control strategy development at pandemic speed.MAbs. 2022 Jan-Dec;14(1):2060724. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2022.2060724. MAbs. 2022. PMID: 35380922 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rathore, A. S. , Winkle, H. Quality by design for biopharmaceuticals. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 9. - PubMed
-
- US Food and Drug Administration . Pharmaceutical cGMPs for the 21st Century—A risk‐based approach. 2004. http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/DevelopmentApprovalProcess/Manufactur....
-
- Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration . PAT Guidance for Industry – A Framework for Innovative Pharmaceutical Development, Manufacturing and Quality Assurance. 2004.
-
- The International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use . ICH harmonised tripartite guideline: Pharmaceutical development Q8(R2). 2009. http://www.ich.org/fileadmin/PublicWebSite/ICHProducts/Guidelines/Qualit....
-
- The International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use . ICH harmonised tripartite guideline: Quality risk management (Q9). 2005. http://www.ich.org/fileadmin/PublicWebSite/ICHProducts/Guidelines/Qualit....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
