The Bottleneck Metaphor of Leadership Culture: How Shared Understandings About Leadership Develop in Groups and Impede Diversity and Effectiveness of Leaders
- PMID: 33716904
- PMCID: PMC7947711
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.635751
The Bottleneck Metaphor of Leadership Culture: How Shared Understandings About Leadership Develop in Groups and Impede Diversity and Effectiveness of Leaders
Abstract
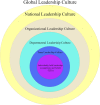
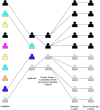
There are two big problems related to leadership today: unequal representation and high failure rates among leaders. This conceptual paper argues that commonly shared values, assumptions, and beliefs about leadership, i.e., universal leadership culture, are the common cause of both problems. After the concepts and levels related to leadership culture were explained, we introduce a multilevel, multi-actor process model named the bottleneck metaphor of leadership culture. This metaphor describes how leadership cultures are co-constructed by multiple actors based on their involvement in leader selection and reproduce themselves in groups over time based on emergent leaders' characteristics. Next, a diagnostic tool called "the leadership mirror" is proposed for organizations that want to assess their leadership culture's current state as a starting point for further interventions. Specific suggestions are made for various actors, ranging from individuals to organizations, for their possible roles in preventing undesired leadership cultures.
Keywords: bottleneck effects; cultural change; diversity in leadership; leadership crisis; leadership emergence; leadership metaphors; organizational culture and climate.
Copyright © 2021 Özcan.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aasland M. S., Skogstad A., Notelaers G., Nielsen M. B., Einarsen S. (2010). The prevalence of destructive leadership behavior. Br. J. Manag. 21, 438–452. 10.1111/j.1467-8551.2009.00672.x - DOI
-
- Acton B. P., Foti R. J., Lord R. G., Gladfelter J. A. (2019). Putting emergence back in leadership emergence: a dynamic, multi-level, process-oriented framework. Leadership Quart. 30, 145–164. 10.1016/j.leaqua.2018.07.002 - DOI
-
- Adams K. A., Crosby A. (2017). The 2016 election, authoritarian childrearing, and our suicidal trajectory. J. Psychohist. 45, 2–11.
-
- Al Ariss A., Özbilgin M., Tatli A., April K. (2014). Tackling Whiteness in organizations and management. J. Managerial Psychol. 29, 362–369. 10.1108/JMP-10-2013-0331 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources