Current Understanding of the Etiology, Symptomatology, and Treatment Options in Premature Ovarian Insufficiency (POI)
- PMID: 33716979
- PMCID: PMC7949002
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2021.626924
Current Understanding of the Etiology, Symptomatology, and Treatment Options in Premature Ovarian Insufficiency (POI)
Abstract
Premature ovarian insufficiency (POI) occurs in at least 1% of all women and causes life-long health problems and psychological stress. Infertility caused by POI used to be considered absolute, with infertility treatment having little or no value. Generally, it has been thought that medicine can provide little service to these patients. The etiology of POI has been found to be genetic, chromosomal, and autoimmune. In addition, the increasing numbers of cancer survivors are candidates for iatrogenic POI, along with patients who have undergone ovarian surgery, especially laparoscopic surgery. Over 50 genes are known to be causally related to POI, and the disease course of some cases has been clarified, but in most cases, the genetic background remains unexplained, suggesting that more genes associated with the etiology of POI need to be discovered. Thus, in most cases, the genetic background of POI has not been clarified. Monosomy X is well known to manifest as Turner's syndrome and is associated with primary amenorrhea, but recent studies have shown that some women with numerical abnormalities of the X chromosome can have spontaneous menstruation up to their twenties and thirties, and some even conceive. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is recommended for women with POI from many perspectives. It alleviates vasomotor and genitourinary symptoms and prevents bone loss and cardiovascular disease. POI has been reported to reduce quality of life and life expectancy, and HRT may help improve both. Most of the problems that may occur with HRT in postmenopausal women do not apply to women with POI; thus, in POI, HRT should be considered physiological replacement of estrogen (+progesterone). This review describes some new approaches to infertility treatment in POI patients that may lead to new treatments for POI, along with the development of more sensitive markers of secondary/preantral follicles and genetic diagnosis.
Keywords: autoimmunity; cardiovascular disease; chromosomal abnormality; genetics; hormone replacement therapy (HRT); ovulation induction; premature ovarian insufficiency (POI); vasomotor symptoms.
Copyright © 2021 Ishizuka.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
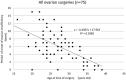
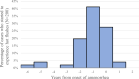
References
-
- ESHRE POI Guideline Development Group . Management of women with premature ovarian insufficiency. Guideline Eur Soc Hum Reprod Embryol (2015) p. 30.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

