Nuclear Receptors in the Control of the NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway
- PMID: 33716981
- PMCID: PMC7947301
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2021.630536
Nuclear Receptors in the Control of the NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway
Abstract
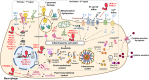
The innate immune system is the first line of defense specialized in the clearing of invaders whether foreign elements like microbes or self-elements that accumulate abnormally including cellular debris. Inflammasomes are master regulators of the innate immune system, especially in macrophages, and are key sensors involved in maintaining cellular health in response to cytolytic pathogens or stress signals. Inflammasomes are cytoplasmic complexes typically composed of a sensor molecule such as NOD-Like Receptors (NLRs), an adaptor protein including ASC and an effector protein such as caspase 1. Upon stimulation, inflammasome complex components associate to promote the cleavage of the pro-caspase 1 into active caspase-1 and the subsequent activation of pro-inflammatory cytokines including IL-18 and IL-1β. Deficiency or overactivation of such important sensors leads to critical diseases including Alzheimer diseases, chronic inflammatory diseases, cancers, acute liver diseases, and cardiometabolic diseases. Inflammasomes are tightly controlled by a two-step activation regulatory process consisting in a priming step, which activates the transcription of inflammasome components, and an activation step which leads to the inflammasome complex formation and the subsequent cleavage of pro-IL1 cytokines. Apart from the NF-κB pathway, nuclear receptors have recently been proposed as additional regulators of this pathway. This review will discuss the role of nuclear receptors in the control of the NLRP3 inflammasome and the putative beneficial effect of new modulators of inflammasomes in the treatment of inflammatory diseases including colitis, fulminant hepatitis, cardiac ischemia-reperfusion and brain diseases.
Keywords: NLRP3; circadian rhythm; inflammasome; inflammation and innate immunity; inflammatory disease; nuclear receptors; therapeutic strategy.
Copyright © 2021 Duez and Pourcet.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hydrogen-Rich Saline Attenuated Subarachnoid Hemorrhage-Induced Early Brain Injury in Rats by Suppressing Inflammatory Response: Possible Involvement of NF-κB Pathway and NLRP3 Inflammasome.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Jul;53(5):3462-3476. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9242-y. Epub 2015 Jun 20. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26091790
-
The LPS/D-Galactosamine-Induced Fulminant Hepatitis Model to Assess the Role of Ligand-Activated Nuclear Receptors on the NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway In Vivo.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1951:189-207. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9130-3_15. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30825154
-
Sendai Virus V Protein Inhibits the Secretion of Interleukin-1β by Preventing NLRP3 Inflammasome Assembly.J Virol. 2018 Sep 12;92(19):e00842-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00842-18. Print 2018 Oct 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 30021903 Free PMC article.
-
Negative regulators and their mechanisms in NLRP3 inflammasome activation and signaling.Immunol Cell Biol. 2017 Aug;95(7):584-592. doi: 10.1038/icb.2017.23. Epub 2017 Mar 30. Immunol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28356568 Review.
-
[Advances in mechanisms for NLRP3 inflammasomes regulation].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2016 Oct;51(10):1505-12. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2016. PMID: 29924571 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Priming from within: TLR2 dependent but receptor independent activation of the mammary macrophage inflammasome by Streptococcus uberis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Oct 11;14:1444178. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1444178. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39463761 Free PMC article.
-
Microglia depletion ameliorates neuroinflammation, anxiety-like behavior, and cognitive deficits in a sex-specific manner in Rev-erbα knockout mice.Brain Behav Immun. 2023 Nov;114:287-298. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2023.08.029. Epub 2023 Aug 28. Brain Behav Immun. 2023. PMID: 37648007 Free PMC article.
-
The innate immune system in human kidney inflammaging.J Nephrol. 2022 Mar;35(2):381-395. doi: 10.1007/s40620-021-01153-4. Epub 2021 Nov 26. J Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 34826123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting NLRP3 Inflammasomes: A Trojan Horse Strategy for Intervention in Neurological Disorders.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Feb;62(2):1840-1881. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04359-2. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 39042218 Review.
-
Natural compounds targeting nuclear receptors for effective cancer therapy.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023 Sep;42(3):765-822. doi: 10.1007/s10555-022-10068-w. Epub 2022 Dec 8. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023. PMID: 36482154 Review.
References
-
- Schmidt FI, Lu A, Chen JW, Ruan J, Tang C, Wu H, et al. . A single domain antibody fragment that recognizes the adaptor ASC defines the role of ASC domains in inflammasome assemblyA VHH defines mechanism of inflammasome assembly. J Exp Med (2016) 213:771–90. 10.1084/jem.20151790 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

