Pre-weaning Ruminal Administration of Differentially-Enriched, Rumen-Derived Inocula Shaped Rumen Bacterial Communities and Co-occurrence Networks of Post-weaned Dairy Calves
- PMID: 33717013
- PMCID: PMC7952535
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.625488
Pre-weaning Ruminal Administration of Differentially-Enriched, Rumen-Derived Inocula Shaped Rumen Bacterial Communities and Co-occurrence Networks of Post-weaned Dairy Calves
Abstract
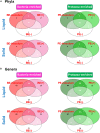
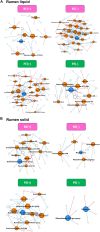
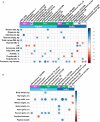
Adult rumen fluid inoculations have been considered to facilitate the establishment of rumen microbiota of pre-weaned dairy calves. However, the sustained effects of the inoculations remain to be explored. In our previous study, 20 pre-weaned dairy calves had been dosed with four types of adult rumen inoculums [autoclaved rumen fluid, bacterial-enriched rumen fluid (BE), protozoal-enriched (PE), and BE + PE] weekly at 3 to 6 weeks of age. To verify the sustained effect of adult rumen inoculation, the rumen bacterial communities, fermentation characteristics, and animal performance measurements were measured after sacrifice from 20 post-weaned dairy bull calves (9 weeks of age). Ruminal pH tended to be lower in BE treated calves (n = 10). All PE treated calves had rumen ciliates (>104 cells per ml of rumen fluid). PE treated calves had greater VFA concentrations (P = 0.052), lower molar proportions of isobutyrate (P = 0.073), and butyrate (P = 0.019) compared to those of control calves. No treatment differences were found in all animal performance measurements. Both PE and BE inocula increased bacterial species richness, Faith's phylogenetic diversity, and Shannon's index in rumen liquid fractions. However, the relative proportion of those bacterial taxa possibly transferred from the donor's rumen was minor. Microbial network analysis showed different co-occurrence and mutually exclusive interactions between treatments of microbial inoculations. Collectively, adult rumen inoculations in pre-weaned dairy calves slightly altered the rumen bacteriome of post-weaned calves without changing fermentation and animal performance.
Keywords: adult rumen inoculation; dairy calves; microbial network; protozoa; rumen bacterial communities.
Copyright © 2021 Park, Cersosimo, Li, Radloff and Zanton.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Bastian M., Heymann S., Jacomy M. (2009). “Gephi: an open source software for exploring and manipulating networks,” in Proceedings of the Third International Aaai Conference on Weblogs and Social Media, San Jose, CA.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

