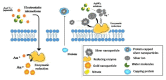
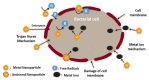
Microbiologically-Synthesized Nanoparticles and Their Role in Silencing the Biofilm Signaling Cascade
- PMID: 33717030
- PMCID: PMC7947885
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.636588
Microbiologically-Synthesized Nanoparticles and Their Role in Silencing the Biofilm Signaling Cascade
Abstract
The emergence of bacterial resistance to antibiotics has led to the search for alternate antimicrobial treatment strategies. Engineered nanoparticles (NPs) for efficient penetration into a living system have become more common in the world of health and hygiene. The use of microbial enzymes/proteins as a potential reducing agent for synthesizing NPs has increased rapidly in comparison to physical and chemical methods. It is a fast, environmentally safe, and cost-effective approach. Among the biogenic sources, fungi and bacteria are preferred not only for their ability to produce a higher titer of reductase enzyme to convert the ionic forms into their nano forms, but also for their convenience in cultivating and regulating the size and morphology of the synthesized NPs, which can effectively reduce the cost for large-scale manufacturing. Effective penetration through exopolysaccharides of a biofilm matrix enables the NPs to inhibit the bacterial growth. Biofilm is the consortia of sessile groups of microbial cells that are able to adhere to biotic and abiotic surfaces with the help extracellular polymeric substances and glycocalyx. These biofilms cause various chronic diseases and lead to biofouling on medical devices and implants. The NPs penetrate the biofilm and affect the quorum-sensing gene cascades and thereby hamper the cell-to-cell communication mechanism, which inhibits biofilm synthesis. This review focuses on the microbial nano-techniques that were used to produce various metallic and non-metallic nanoparticles and their "signal jamming effects" to inhibit biofilm formation. Detailed analysis and discussion is given to their interactions with various types of signal molecules and the genes responsible for the development of biofilm.
Keywords: antibiofilm; micronanotechnique; nanoparticles; quorum quencher; quorum-sensing.
Copyright © 2021 Lahiri, Nag, Sheikh, Sarkar, Edinur, Pati and Ray.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abinaya M., Vaseeharan B., Divya M., Sharmili A., Govindarajan M., Alharbi N. S., et al. (2018). Bacterial exopolysaccharide (EPS)-coated ZnO nanoparticles showed high antibiofilm activity and larvicidal toxicity against malaria and Zika virus vectors. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 45, 93–103. 10.1016/j.jtemb.2017.10.002 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ahmed E., Kalathil S., Shi L., Alharbi O., Wang P. (2018). Synthesis of ultra-small platinum, palladium and gold nanoparticles by Shewanella loihica PV-4 electrochemically active biofilms and their enhanced catalytic activities. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 22, 919–929. 10.1016/j.jscs.2018.02.002 - DOI
-
- Al-Shabib N. A., Husain F. M., Hassan I., Khan M. S., Ahmed F., Qais F. A., et al. (2018). Biofabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticle from Ochradenus baccatus leaves: broad-spectrum antibiofilm activity, protein binding studies and in vivo toxicity and stress studies. J. Nanomater. 2018:8612158. 10.1155/2018/8612158 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources