New Insights Into the Antibacterial Mechanism of Cryptotanshinone, a Representative Diterpenoid Quinone From Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge
- PMID: 33717044
- PMCID: PMC7950322
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.647289
New Insights Into the Antibacterial Mechanism of Cryptotanshinone, a Representative Diterpenoid Quinone From Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge
Abstract
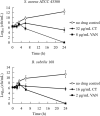
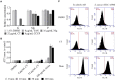
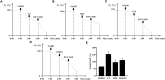
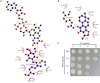
The rapid rise of antibiotic resistance causes an urgent need for new antimicrobial agents with unique and different mechanisms of action. The respiratory chain is one such target involved in the redox balance and energy metabolism. As a natural quinone compound isolated from the root of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge, cryptotanshinone (CT) has been previously demonstrated against a wide range of Gram-positive bacteria including multidrug-resistant pathogens. Although superoxide radicals induced by CT are proposed to play an important role in the antibacterial effect of this agent, its mechanism of action is still unclear. In this study, we have shown that CT is a bacteriostatic agent rather than a bactericidal agent. Metabolome analysis suggested that CT might act as an antibacterial agent targeting the cell membrane. CT did not cause severe damage to the bacterial membrane but rapidly dissipated membrane potential, implying that this compound could be a respiratory chain inhibitor. Oxygen consumption analysis in staphylococcal membrane vesicles implied that CT acted as respiratory chain inhibitor probably by targeting type II NADH:quinone dehydrogenase (NDH-2). Molecular docking study suggested that the compound would competitively inhibit the binding of quinone to NDH-2. Consistent with the hypothesis, the antimicrobial activity of CT was blocked by menaquinone, and the combination of CT with thioridazine but not 2-n-heptyl-4-hydroxyquinoline-N-oxide exerted synergistic activity against Staphylococcus aureus. Additionally, combinations of CT with other inhibitors targeting different components of the bacterial respiratory chain exhibit potent synergistic activities against S. aureus, suggesting a promising role in combination therapies.
Keywords: cryptotanshinone; menaquinone; metabolome analysis; respiratory chain inhibitor; type II NADH:quinone dehydrogenase.
Copyright © 2021 Chen, Ding, Dai, Chen, Gong, Ma and Qian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Al-Mebairik N. F., El-Kersh T. A., Al-Sheikh Y. A., Marie M. A. M. (2016). A review of virulence factors, pathogenesis, and antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Rev. Med. Microbiol. 27 50–56. 10.1097/MRM.0000000000000067 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

