Targeting miR-148b-5p Inhibits Immunity Microenvironment and Gastric Cancer Progression
- PMID: 33717068
- PMCID: PMC7944991
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.590447
Targeting miR-148b-5p Inhibits Immunity Microenvironment and Gastric Cancer Progression
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have been discovered to dictate the development of various tumors. However, studies on the roles of miRNAs in the progression of gastric cancer (GC) are still lacking.
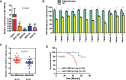
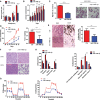
Methods: Herein, by analyzing GC cell lines and patients samples, we observed that miR-148b-5p was significantly downregulated in GC. We also confirmed that miR-148b-5p overexpression significantly inhibited GC cell proliferation and invasion in vitro and in vivo.
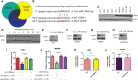
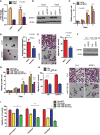
Results: Overexpression of miR-148b-5p not only reprogrammed the metabolic properties of GC but also regulated the immune microenvironment by shifting lymphocyte and myeloid populations. Mechanistically, ATPIF1, an important glycolysis-associated gene, was identified as a direct target of miR-148b-5p and mediated the effect of miR-148b-5p. Notably, the low level of miR-148b-5p was significantly related with poor prognosis of GC patients (P < 0.001). Importantly, the levels of miR-148b-5p significantly changed the sensitivity of GC cells to several anti-cancer drugs (Doxorubicin, P < 0.05, Paclitaxel, P < 0.01, Docetaxel, P < 0.05).
Conclusions: Targeting miR-148b-5p inhibits immunity microenvironment and gastric cancer progression.
Keywords: ATPIF1; gastric cancer; immune microenvironment; metabolic reprogramming; miR-148b-5p.
Copyright © 2021 Zhang, Huo, Sun, Wu, Zhang, Wang, Wang, Wei, Qu, Cao and Jiang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

