Major Role of the IL17/23 Axis in Psoriasis Supports the Development of New Targeted Therapies
- PMID: 33717124
- PMCID: PMC7948519
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.621956
Major Role of the IL17/23 Axis in Psoriasis Supports the Development of New Targeted Therapies
Abstract
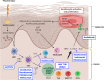
Psoriasis is a frequent, chronic disease characterized by cutaneous inflammatory plaques and/or arthritis. It may be associated with few other diseases, mainly Crohn's disease and metabolic syndrome. The medical and psychosocial burden of psoriasis remains high even since biological treatments arose, stressing that efforts to decipher its physiopathology are constantly needed. Tumor-necrosis factor α, interleukin (IL) 12 and IL17 have been previously associated with psoriasis and successfully targeted by monoclonal antibodies. IL17 in particular has been initially described as a T helper (Th) 17-produced cytokine, but it is now established that other cell types, such as γδ T lymphocytes, Mucosal-Associated Invariant T (MAIT) cells and Innate Lymphoïd Cells (ILC) 3 are also important sources of IL17 in the skin in response to inflammatory stimuli. Th17 phenotype has been shown to be stabilized by IL23, which is synthetized by macrophages and dendritic cells in response to Toll Like Receptors and C-type Lectin Receptors stimulation. Recent data also reported a crucial role for IL23 in MAIT17 and ILC3 homeostasis. Genome-wide association studies have found a significant link between IL23 receptor polymorphism and psoriasis susceptibility. IL23 signals through Janus kinase 2 and Tyrosine kinase 2, against which specific inhibitors are currently being tested. Monoclonal antibodies against IL17 and IL23 are only the beginning of a new avenue in psoriasis treatment. This review focuses on the molecular basis underlying IL23/IL17 axis blockade in psoriasis, and on future targets in this pathway.
Keywords: IL17; IL23; Th17; psoriasis; skin.
Copyright © 2021 Bugaut and Aractingi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Parisi R, Symmons DPM, Griffiths CEM, Ashcroft DM. Identification and Management of Psoriasis and Associated ComorbidiTy (IMPACT) project team. Global epidemiology of psoriasis: a systematic review of incidence and prevalence. J Invest Dermatol (2013) 133(2):377–85. 10.1038/jid.2012.339 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Augustin M, Dauden E, Mrowietz U, Konstantinou MP, Gerdes S, Rissler M, et al. . Baseline characteristics of patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis according to previous systemic treatment exposure: the PROSE study population. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol (2020) 34(11):2548–56. 10.1111/jdv.16400 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

