NLRP3 Deficiency Protects Against Intermittent Hypoxia-Induced Neuroinflammation and Mitochondrial ROS by Promoting the PINK1-Parkin Pathway of Mitophagy in a Murine Model of Sleep Apnea
- PMID: 33717152
- PMCID: PMC7943742
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.628168
NLRP3 Deficiency Protects Against Intermittent Hypoxia-Induced Neuroinflammation and Mitochondrial ROS by Promoting the PINK1-Parkin Pathway of Mitophagy in a Murine Model of Sleep Apnea
Abstract
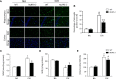
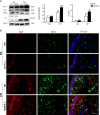
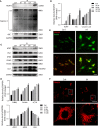
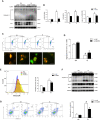
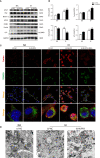
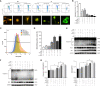
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) associated neurocognitive impairment is mainly caused by chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH)-triggered neuroinflammation and oxidative stress. Previous study has demonstrated that mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (mtROS) was pivotal for hypoxia-related tissue injury. As a cytosolic multiprotein complex that participates in various inflammatory and neurodegenerative diseases, NLRP3 inflammasome could be activated by mtROS and thereby affected by the mitochondria-selective autophagy. However, the role of NLRP3 and possible mitophagy mechanism in CIH-elicited neuroinflammation remain to be elucidated. Compared with wild-type mice, NLRP3 deficiency protected them from CIH-induced neuronal damage, as indicated by the restoration of fear-conditioning test results and amelioration of neuron apoptosis. In addition, NLRP3 knockout mice displayed the mitigated microglia activation that elicited by CIH, concomitantly with elimination of damaged mitochondria and reduction of oxidative stress levels (malondialdehyde and superoxide dismutase). Elevated LC3 and beclin1 expressions were remarkably observed in CIH group. In vitro experiments, intermittent hypoxia (IH) significantly facilitated mitophagy induction and NLRP3 inflammasome activation in microglial (BV2) cells. Moreover, IH enhanced the accumulation of damaged mitochondria, increased mitochondrial depolarization and augmented mtROS release. Consistently, NLRP3 deletion elicited a protective phenotype against IH through enhancement of Parkin-mediated mitophagy. Furthermore, Parkin deletion or pretreated with 3MA (autophagy inhibitor) exacerbated these detrimental actions of IH, which was accompanied with NLRP3 inflammasome activation. These results revealed NLRP3 deficiency acted as a protective promotor through enhancing Parkin-depended mitophagy in CIH-induced neuroinflammation. Thus, NLRP3 gene knockout or pharmacological blockage could be as a potential therapeutic strategy for OSA-associated neurocognitive impairment.
Keywords: neuroinflammation; nucleotide‐binding domain like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3); obstructive sleep apnea (OSA); parkin-mediated mitophagy; reactive oxygen species (ROS).
Copyright © 2021 Wu, Gong, Xie, Gu, Wang, Liu and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

