Nuclear Receptors as Multiple Regulators of NLRP3 Inflammasome Function
- PMID: 33717162
- PMCID: PMC7952630
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.630569
Nuclear Receptors as Multiple Regulators of NLRP3 Inflammasome Function
Abstract
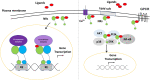
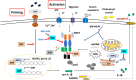
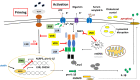
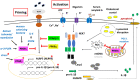
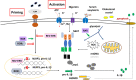
Nuclear receptors are important bridges between lipid signaling molecules and transcription responses. Beside their role in several developmental and physiological processes, many of these receptors have been shown to regulate and determine the fate of immune cells, and the outcome of immune responses under physiological and pathological conditions. While NLRP3 inflammasome is assumed as key regulator for innate and adaptive immune responses, and has been associated with various pathological events, the precise impact of the nuclear receptors on the function of inflammasome is hardly investigated. A wide variety of factors and conditions have been identified as modulators of NLRP3 inflammasome activation, and at the same time, many of the nuclear receptors are known to regulate, and interact with these factors, including cellular metabolism and various signaling pathways. Nuclear receptors are in the focus of many researches, as these receptors are easy to manipulate by lipid soluble molecules. Importantly, nuclear receptors mediate regulatory mechanisms at multiple levels: not only at transcription level, but also in the cytosol via non-genomic effects. Their importance is also reflected by the numerous approved drugs that have been developed in the past decade to specifically target nuclear receptors subtypes. Researches aiming to delineate mechanisms that regulate NLRP3 inflammasome activation draw a wide range of attention due to their unquestionable importance in infectious and sterile inflammatory conditions. In this review, we provide an overview of current reports and knowledge about NLRP3 inflammasome regulation from the perspective of nuclear receptors, in order to bring new insight to the potentially therapeutic aspect in targeting NLRP3 inflammasome and NLRP3 inflammasome-associated diseases.
Keywords: IL-1β; LXR; NLRP3; PPAR; PXR; inflammasome; metabolism; signaling.
Copyright © 2021 Alatshan and Benkő.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

