Effect and related mechanism of Yinchenhao decoction on mice with lithogenic diet-induced cholelithiasis
- PMID: 33717259
- PMCID: PMC7885065
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2021.9747
Effect and related mechanism of Yinchenhao decoction on mice with lithogenic diet-induced cholelithiasis
Abstract
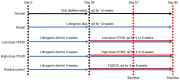
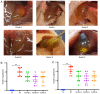
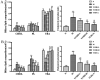
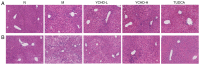
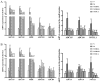
The aim of the present study was to investigate the effects and the underlying mechanisms of Yinchenhao Decoction (YCHD), a traditional Chinese medicine formulation, on C57BL/6 mice with lithogenic diet (LD)-induced cholelithiasis. The condition of cholelithiasis was evaluated using a six-level criteria. Levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), total cholesterol (TC), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in the serum and liver tissue were measured using enzyme colorimetry. Concentrations of TC, phospholipids (PL) and total bile acids (TBA) in the bile were measured to calculate the cholesterol saturation index. Liver histopathology was microscopically observed and mRNA expression levels of ABCG5, ABCG8, SRBI, ABCB4, ABCB11 and NPC1L1 involved in cholesterol metabolism were measured using reverse transcription-quantitative PCR. The results showed that feeding mice the LD induced cholelithiasis, along with abnormal serum biochemical indices and imbalances in biliary cholesterol homeostasis. Increased ALT and ALP levels in the serum and ALT, ALP, TC and LDL-C levels in the serum and liver indicated the existence of hepatocyte injury, which were consistent with the pathological changes. YCHD treatment ameliorated the serum and hepatic biochemical abnormalities and adjusted the biliary imbalance. In addition, elevated expression of ATP-binding cassette subfamily G member 5/8, scavenger receptor class B type I and Niemann-Pick C1 Like 1 in the liver and small intestine were observed at the onset of cholelithiasis but were reversed by YCHD. Taken together, results from the present study suggest that YCHD ameliorated LD-induced cholelithiasis mice, which may be caused by improvements in biliary cholesterol supersaturation and regulation of cholesterol metabolism.
Keywords: Yinchenhao decoction; biliary cholesterol supersaturation; cholelithiasis; cholesterol metabolism.
Copyright: © Zhou et al.
Figures
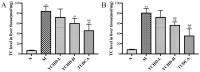
Similar articles
-
Protective Effects of Yinchenhao Decoction on Cholesterol Gallstone in Mice Fed a Lithogenic Diet by Regulating LXR, CYP7A1, CYP7B1, and HMGCR Pathways.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018 Sep 17;2018:8134918. doi: 10.1155/2018/8134918. eCollection 2018. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018. PMID: 30310412 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal CREBH overexpression prevents high-cholesterol diet-induced hypercholesterolemia by reducing Npc1l1 expression.Mol Metab. 2016 Sep 17;5(11):1092-1102. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2016.09.004. eCollection 2016 Nov. Mol Metab. 2016. PMID: 27818935 Free PMC article.
-
Yinchenhao decoction attenuates obstructive jaundice-induced liver injury and hepatocyte apoptosis by suppressing protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase-induced pathway.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Nov 7;25(41):6205-6221. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i41.6205. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31749592 Free PMC article.
-
ABCG5/ABCG8 in cholesterol excretion and atherosclerosis.Clin Chim Acta. 2014 Jan 20;428:82-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.11.010. Epub 2013 Nov 16. Clin Chim Acta. 2014. PMID: 24252657 Review.
-
Biliary cholesterol secretion: more than a simple ABC.World J Gastroenterol. 2010 Dec 21;16(47):5936-45. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i47.5936. World J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 21157969 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The mechanism of Yinchenhao decoction in treating obstructive-jaundice-induced liver injury based on Nrf2 signaling pathway.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Aug 28;28(32):4635-4648. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i32.4635. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36157920 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements in Managing Choledocholithiasis and Acute Cholangitis in the Elderly: A Comprehensive Review.Cureus. 2025 Feb 4;17(2):e78492. doi: 10.7759/cureus.78492. eCollection 2025 Feb. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40051943 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of ursodeoxycholic acid in the bile biochemistry and metabolomics in patients with choledocholithiasis: a prospective study.Metabolomics. 2022 Jul 1;18(7):46. doi: 10.1007/s11306-022-01906-7. Metabolomics. 2022. PMID: 35778620 Clinical Trial.
-
Comprehensive Effect of Carbon Tetrachloride and Reversal of Gandankang Formula in Mice Liver: Involved in Oxidative Stress, Excessive Inflammation, and Intestinal Microflora.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Nov 12;11(11):2234. doi: 10.3390/antiox11112234. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36421420 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cremer A, Arvanitakis M. Diagnosis and management of bile stone disease and its complications. Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol. 2016;62:103–129. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
