The miR-136-5p/ROCK1 axis suppresses invasion and migration, and enhances cisplatin sensitivity in head and neck cancer cells
- PMID: 33717260
- PMCID: PMC7885062
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2021.9748
The miR-136-5p/ROCK1 axis suppresses invasion and migration, and enhances cisplatin sensitivity in head and neck cancer cells
Abstract
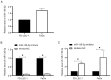
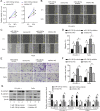
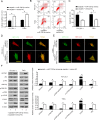
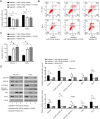
Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC) and hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (HPSCC) are two types of head and neck cancers with high incidence rates and relatively poor prognoses. The aim of the present study was to determine the effects of microRNA (miR/miRNA)-136-5p and its downstream target, Rho-associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase 1 (ROCK1), on LSCC and HPSCC progression and cisplatin sensitivity. The miRNA and protein expression levels in head and neck cancer cell lines were evaluated using reverse transcription-quantitative PCR and western blotting, respectively. MTT, wound healing assays, transwell assays and flow cytometry analysis were performed to measure cell properties. The binding between miR-136-5p and ROCK1 was detected using a dual-luciferase reporter assay. Autophagy double-labeled adenoviral infection assays were used to assess cell autophagy. The results showed that miR-136-5p was expressed in LSCC and HPSCC cells. Functional experiments showed that the expression of miR-136-5p in LSCC and HPSCC cells was negatively correlated with cell viability, invasion and migration. Additionally, miR-136-5p overexpression inhibited epithelial-mesenchymal transition, whereas miR-136-5p knockdown had the opposite effect. Dual-luciferase reporter assays confirmed the targeting relationship between miR-136-5p and ROCK1. miR-136-5p overexpression increased the cisplatin sensitivity of LSCC and HPSCC cells by reducing cell viability, as well as promoting cell apoptosis and autophagy. miR-136-5p overexpression decreased the expression levels of its downstream target ROCK1 and attenuated activity of the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in cisplatin-treated LSCC and HPSCC cells. Conversely, miR-136-5p knockdown increased ROCK1 levels and decreased cisplatin sensitivity of the LSCC and HPSCC cells by increasing cell viability and inhibiting cell apoptosis, which was reversed by ROCK1 inhibition using the ROCK1 inhibitor, Y27632. Taken together, the results showed that the miR-136-5p/ROCK1 axis inhibits cell invasion and migration, and increases the sensitivity of LSCC and HPSCC cells to cisplatin.
Keywords: Rho-associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase 1; cell invasion; cell migration; cisplatin sensitivity; hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma; laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma; microRNA-136-5p.
Copyright: © Yang et al.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes the malignancy of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma by regulating the microRNA-204-5p/SEMA4B axis.Oncol Lett. 2021 Nov;22(5):802. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.13063. Epub 2021 Sep 23. Oncol Lett. 2021. Retraction in: Oncol Lett. 2023 Nov 13;27(1):15. doi: 10.3892/ol.2023.14148. PMID: 34630709 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Regulating of cell cycle progression by the lncRNA CDKN2B-AS1/miR-324-5p/ROCK1 axis in laryngeal squamous cell cancer.Int J Biol Markers. 2020 Mar;35(1):47-56. doi: 10.1177/1724600819898489. Epub 2020 Jan 21. Int J Biol Markers. 2020. PMID: 31960744
-
Hsa_circ_0042823 accelerates cancer progression via miR-877-5p/FOXM1 axis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.Ann Med. 2021 Dec;53(1):960-970. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2021.1934725. Ann Med. 2021. PMID: 34124974 Free PMC article.
-
The knockdown of SNHG3 inhibits the progression of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma by miR-340-5p/YAP1 axis and Wnt/β-catenin pathway.Neoplasma. 2020 Sep;67(5):1094-1105. doi: 10.4149/neo_2020_191022N1073. Epub 2020 Jun 16. Neoplasma. 2020. PMID: 32538668
-
MicroRNA-383: A tumor suppressor miRNA in human cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Oct 13;10:955486. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.955486. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36313570 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Metastasis: Focus on Laryngeal Carcinoma.Biomedicines. 2022 Sep 1;10(9):2148. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10092148. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36140250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CircRNA PDE3B regulates tumorigenicity via the miR-136-5p/MAP3K2 axis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Histol Histopathol. 2023 Sep;38(9):1029-1041. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-567. Epub 2022 Dec 1. Histol Histopathol. 2023. PMID: 36533720
-
CircPRRC2C Promotes the Oncogenic Phenotypes of Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells via MiR-136-5p/HOXD11 Axis.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Sep;66(9):2381-2395. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00868-y. Epub 2023 Sep 20. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37728841
-
Long non-coding RNA DSCAM-AS1 promotes pancreatic cancer progression via regulating the miR-136-5p/PBX3 axis.Bioengineered. 2022 Feb;13(2):4153-4165. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2016326. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35142595 Free PMC article.
-
Research and progress of microRNA-136 in metastatic tumors.Front Oncol. 2025 Mar 4;15:1555270. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1555270. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40104500 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Grégoire V, Lefebvre JL, Licitra L, Felip E. Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: EHNS-ESMO-ESTRO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2010;21 (Suppl 5):v184–v186. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdq185. EHNS-ESMO-ESTRO Guidelines Working Group. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
