Contrast-induced encephalopathy in an infant
- PMID: 33717383
- PMCID: PMC7921186
- DOI: 10.1016/j.radcr.2021.02.028
Contrast-induced encephalopathy in an infant
Erratum in
-
Erratum regarding missing Declaration of Competing Interest statements in previously published articles.Radiol Case Rep. 2022 Sep 29;17(12):4933. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2022.08.054. eCollection 2022 Dec. Radiol Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 36311872 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Contrast-induced encephalopathy (CIE) is a well-known but rare complication following contrast media administration. Its nonspecific clinical manifestations hinder diagnosis, particularly in the pediatric population. The majority of cases are reversible, with clinical improvement and resolution of signs noted on diagnostic imaging. Here, we report the case of a 2-month-old patient with a history of complex cardiovascular disease who presented with a single episode of seizure after undergoing cardiac catheterization with nonionic iodinated contrast media. CIE is diagnosed based on the signs and symptoms exhibited by the patient and the findings on plain head computed tomography (CT) scan. Subsequently, the absence of neurological symptoms and disappearance of the imaging alterations on a control CT are documented.
Keywords: Blood–brain barrier; Contrast medium; Encephalopathy; Neurotoxicity.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. on behalf of University of Washington.
Figures
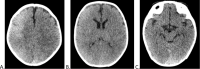
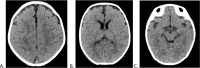
References
-
- Frye R, Newburger J, Nugent A, Sahin M. Focal seizure and cerebral contrast retention after cardiac catheterization. Pediatr Neurol. 2005;32:213–216. - PubMed
-
- Torvik A, Walday P. Neurotoxicity of water -soluble contrast media. Acta Radiológica. 1995;36:221–229. - PubMed
-
- Dominguez Ortega F, González Azpeitia G, Cidras Pidre M, Calvo Rosales J. Apertura reversible de la barrera hematoencefálica inducida por hipercapnia en hiperbilirrubinemia experimental. An Esp Pediatr. 1997;46:374–377. - PubMed
-
- Haussen DC, Modir R, Yavagal DR. Unilateral contrast neurotoxicity as a stroke mimic after cerebral angiogram. J Neuroimaging. 2011;XX:1–3. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

