Successful embolization of giant pulmonary artery pseudoaneurysm using coils and ethylene vinyl alcohol copolymer (Onyx)
- PMID: 33717384
- PMCID: PMC7921184
- DOI: 10.1016/j.radcr.2021.02.029
Successful embolization of giant pulmonary artery pseudoaneurysm using coils and ethylene vinyl alcohol copolymer (Onyx)
Erratum in
-
Erratum regarding missing Declaration of Competing Interest statements in previously published articles.Radiol Case Rep. 2022 Sep 29;17(12):4933. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2022.08.054. eCollection 2022 Dec. Radiol Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 36311872 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Hemoptysis could be a life-threatening event, especially when the bleeding originates from the arterial pulmonary circulation. The main cause of this type of bleeding is pulmonary artery pseudoaneurysm (PAP), which can be managed by surgical, medical or minimally invasive techniques. This study reports the case of massive hemoptysis in a 75-year-old male patient, with a former history of lobectomy. The initial CT scan showed a giant PAP from a branch of the right middle lobar pulmonary artery, within the right lower lobectomy cavity. An endovascular approach was decided. Subsequently, the feeding artery of the PAP was embolized with detachable coils. The control CT scan showed a persistent opacification of the PAP. The embolization was then completed by injection of Onyx within coils packing, with a complete thrombose of the PAP on control CT scan. This report confirms the safety and efficacy profile of an endovascular approach to treat giant PAP, using a combination of coils and Onyx.
Keywords: Embolization; Hemoptysis; Lung; Pulmonary artery pseudoaneurysm.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. on behalf of University of Washington.
Figures
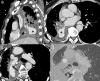
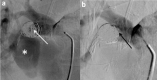
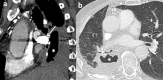
References
-
- Remy J, Lemaitre L, Lafitte J, Vilain M, Saint Michel J, Steenhouwer F. Massive hemoptysis of pulmonary arterial origin: diagnosis and treatment. Am J Roentgenol. 1984;143:963–969. - PubMed
-
- Khalil A, Fartoukh M, Tassart M, Parrot A, Marsault C, Carette M-F. Role of MDCT in identification of the bleeding site and the vessels causing hemoptysis. Am J Roentgenol. 2007;188:W117–W125. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Gilman MD, Humphrey KL, Salazar GM, Sharma A, Muniappan A. Pulmonary artery pseudoaneurysms: clinical features and CT findings. Am J Roentgenol. 2017;208:84–91. - PubMed
-
- Merlino J, Temes RT, Joste NE, Gill IS. Invasive pulmonary mucormycosis with ruptured pseudoaneurysm. Ann Thorac Surg. 2003;75:1332. - PubMed
-
- Lal A, Bansal A, Chaluvashetty SB, Sandhu MS, Gorsi U. Percutaneous transthoracic embolisation for massive haemoptysis secondary to peripheral pulmonary artery pseudoaneurysms. Eur Radiol. 2020 http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00330-020-07348-w [cited 2020 Dec 26]; Available from. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

