Cardiovascular Injury Due to SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 33717830
- PMCID: PMC7934983
- DOI: 10.1007/s40588-021-00160-0
Cardiovascular Injury Due to SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
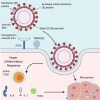
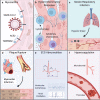
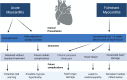
Purpose of review: The world is currently facing the largest global health crisis since the early 1900s due to a novel coronavirus. While SARS-CoV-2 infection causes predictable symptoms in COVID-19 patients, including upper respiratory distress and fever, the heterogeneity of manifestations is surprising. This review focuses on direct and indirect causes of myocardial injury in COVID-19 patients and highlights current knowledge, treatment strategies, and outstanding questions in the field.
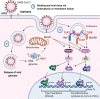
Recent findings: Data are emerging that highlight the extent of cardiovascular involvement in COVID-19 patients, including evidence that SARS-CoV-2 causes myocarditis and increases cardiac risk. The incidence of cardiac injury is much greater in patients with severe disease presentation and those in intensive care.
Summary: During the past year, COVID-19 patient mortality rates have improved due to tailored pharmacological treatments and patient management strategies that address the unique presentation of symptoms, which will hopefully also reduce the incidence of cardiac injury.
Keywords: Cardiac injury; Arrhythmia; COVID-19; Cardiomyopathy; Myocarditis.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Switzerland AG part of Springer Nature 2021.
Figures
References
-
- Zhou P, Yang XL, Wang XG, Hu B, Zhang L, Zhang W, Si HR, Zhu Y, Li B, Huang CL, Chen HD, Chen J, Luo Y, Guo H, Jiang RD, Liu MQ, Chen Y, Shen XR, Wang X, Zheng XS, Zhao K, Chen QJ, Deng F, Liu LL, Yan B, Zhan FX, Wang YY, Xiao GF, Shi ZL. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature. 2020;579(7798):270–273. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, Song J, Zhao X, Huang B, Shi W, Lu R, Niu P, Zhan F, Ma X, Wang D, Xu W, Wu G, Gao GF, Tan W, China Novel Coronavirus Investigating and Research Team A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(8):727–733. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001017. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
