Current Advances in Black Phosphorus-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 33717847
- PMCID: PMC7927632
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202003033
Current Advances in Black Phosphorus-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Cancer Therapy
Abstract
Cancer has been one of the major threats to the lives of human beings for centuries. Traditional therapy is more or less faced with certain defects, such as poor targeting, easy degradation, high side effects, etc. Therefore, in order to improve the treatment efficiency of drugs, an intelligent drug delivery system (DDS) is considered as a promising solution strategy. Due to their special structure and large specific surface area, 2D materials are considered to be a good platform for drug delivery. Black phosphorus (BP), as a new star of the 2D family, is recommended to have the potential to construct DDS by virtue of its outstanding photothermal therapy (PTT), photodynamic therapy (PDT), and biodegradable properties. This tutorial review is intended to provide an introduction of the current advances in BP-based DDSs for cancer therapy, which covers topics from its construction, classified by the types of platforms, to the stimuli-responsive controlled drug release. Moreover, their cancer therapy applications including mono-, bi-, and multi-modal synergistic cancer therapy as well as the research of biocompatibility are also discussed. Finally, the current status and future prospects of BP-based DDSs for cancer therapy are summarized.
Keywords: biocompatibility; black phosphorus; cancer therapy; drug delivery; stimuli‐responsive release.
© 2021 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


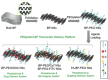
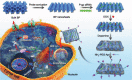
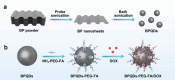
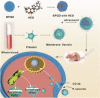





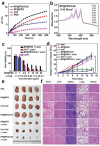
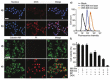


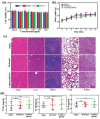
References
-
- Keca J., Chen J., Overchuk M., Muhanna N., Maclaughlin C., Jin C., Foltz W., Irish J., Zheng G., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 6187. - PubMed
-
- Huynh E., Leung B., Helfield B., Shakiba M., Gandier J., Jin C., Master E., Wilson B., Goertz D., Zheng G., Nat. Nanotechnol. 2015, 10, 325. - PubMed
-
- Lee N., Choi S., Hyeon T., Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2641. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y., Ai K., Liu J., Yuan Q., He Y., Lu L., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 1437. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
