The difference of social cognitive and neurocognitive performance between patients with schizophrenia at different stages and influencing factors
- PMID: 33718008
- PMCID: PMC7933534
- DOI: 10.1016/j.scog.2021.100195
The difference of social cognitive and neurocognitive performance between patients with schizophrenia at different stages and influencing factors
Abstract
Objects: To explore the specific features of cognitive function in patients with schizophrenia at different stages and its influencing factors.
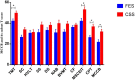
Methods: The MATRICS Consensus Cognitive Battery (MCCB) and the Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale (BPRS) were administered to 208 patients with schizophrenia, including 158 clinically stable schizophrenia (CSS) and 50 first-episode patients with schizophrenia (FES), and 40 healthy controls (HC). Propensity score matching (PSM) was used to match the CSS and FES.
Results: (1) The MCCB and it,s sub-scale scores in patients with schizophrenia were lower than HC, but the score of emotion intelligence showed no significant difference between CSS and HC. (2) Before PSM, the cognitive scores of FES were significantly lower than CSS (except trail making A test, Hopkins verbal learning, category fluency). After PSM, patients with CSS still do better in performing trail making A test, emotional intelligence, continuous performances and MCCB total score. (3) BPRS total score, gender, group (FES vs CSS) and age were independent contributors to emotion intelligence, and BPRS total score had the biggest effect. (4) The effect of group (FES vs CSS) on MCCB total score and emotional intelligence was statistically significant.
Conclusions: There are significant cognitive deficits in patients with FES and CSS compared with HC. FES have greater cognitive impairments compared with CSS. Emotion intelligence of CSS may be even close to the level of HC. BPRS total score, gender, group (FES vs CSS) and age may be the independent contributors to social cognition. Group (FES vs CSS) may play an important effect on general cognition and social cognition.
Keywords: Influencing factors; MCCB; Neurocognition; Schizophrenia; Social cognition.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest in relation to this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Meta-analysis of cognitive function in Chinese first-episode schizophrenia: MATRICS Consensus Cognitive Battery (MCCB) profile of impairment.Gen Psychiatr. 2019 Jul 22;32(3):e100043. doi: 10.1136/gpsych-2018-100043. eCollection 2019. Gen Psychiatr. 2019. PMID: 31423473 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive impairments in first-episode drug-naive and chronic medicated schizophrenia: MATRICS consensus cognitive battery in a Chinese Han population.Psychiatry Res. 2016 Apr 30;238:196-202. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2016.02.042. Epub 2016 Feb 18. Psychiatry Res. 2016. PMID: 27086233
-
Gender differences in cognitive performance among young adults with first-episode schizophrenia in China.Schizophr Res Cogn. 2025 Feb 15;40:100353. doi: 10.1016/j.scog.2025.100353. eCollection 2025 Jun. Schizophr Res Cogn. 2025. PMID: 40028175 Free PMC article.
-
Use of the Chinese version of the MATRICS Consensus Cognitive Battery to assess cognitive functioning in individuals with high risk for psychosis, first-episode schizophrenia and chronic schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Lancet Reg Health West Pac. 2024 Feb 9;45:101016. doi: 10.1016/j.lanwpc.2024.101016. eCollection 2024 Apr. Lancet Reg Health West Pac. 2024. PMID: 38699289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The International Society for Bipolar Disorders-Battery for Assessment of Neurocognition (ISBD-BANC).Bipolar Disord. 2010 Jun;12(4):351-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-5618.2010.00830.x. Bipolar Disord. 2010. PMID: 20636632 Review.
Cited by
-
Examining associations, moderators and mediators between childhood maltreatment, social functioning, and social cognition in psychotic disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Psychol Med. 2023 Oct;53(13):5909-5932. doi: 10.1017/S0033291723001678. Epub 2023 Jul 17. Psychol Med. 2023. PMID: 37458216 Free PMC article.
-
rTMS Induces Brain Functional and Structural Alternations in Schizophrenia Patient With Auditory Verbal Hallucination.Front Neurosci. 2021 Sep 1;15:722894. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.722894. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34539338 Free PMC article.
-
A cross-sectional analysis of registry data of severe mental disorders in Fuzhou, China: current status and prospects.BMC Psychiatry. 2022 Dec 14;22(1):790. doi: 10.1186/s12888-022-04364-6. BMC Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36517752 Free PMC article.
-
Emotional Processing Profile in Patients with First Episode Schizophrenia: The Influence of Neurocognition.J Clin Med. 2022 Apr 6;11(7):2044. doi: 10.3390/jcm11072044. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35407652 Free PMC article.
-
A nation-wide twin study of social cognition in schizophrenia spectrum disorders.Schizophrenia (Heidelb). 2022 Mar 2;8(1):12. doi: 10.1038/s41537-022-00223-1. Schizophrenia (Heidelb). 2022. PMID: 35236855 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdel-Hamid M., Lehmkamper C., Sonntag C., Juckel G., Daum I., Brune M. Theory of mind in schizophrenia: the role of clinical symptomatology and neurocognition in understanding other people’s thoughts and intentions. Psychiatry Res. 2009;165(1–2):19–26. - PubMed
-
- Bechi M., Agostoni G., Buonocore M., Bosinelli F., Spangaro M., Bianchi L. The influence of premorbid adjustment and autistic traits on social cognitive dysfunction in schizophrenia. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2020;26(3):276–285. - PubMed
-
- Bora E. Peripheral inflammatory and neurotrophic biomarkers of cognitive impairment in schizophrenia: a meta-analysis. Psychol. Med. 2019;49(12):1971–1979. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

