Comprehensive genomic profiling of combined small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 33718010
- PMCID: PMC7947408
- DOI: 10.21037/tlcr-20-1099
Comprehensive genomic profiling of combined small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Combined small cell lung cancer (CSCLC) is an uncommon and heterogeneous subtype of small cell lung cancer (SCLC). However, there is limited data concerning the different molecular changes and clinical features in CSCLC compared to pure SCLC.
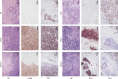
Methods: The clinical and pathological characteristics of pure SCLC and CSCLC patients were analyzed. Immunohistochemistry and microdissection were performed to isolate the CSCLC components. Further molecular analysis was carried out by next-generation sequencing (NGS) in 12 CSCLC and 30 pure SCLC.
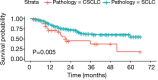
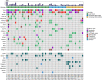
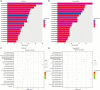
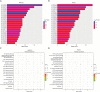
Results: There were no significant differences in clinical features between CSCLC and pure SCLC. Overall survival (OS) of CSCLC patients was worse than pure SCLC (P=0.005). NGS results indicated that TP53 and RB1 were the most frequently mutated genes in both CSCLC (83.33% and 66.67%) and pure SCLC (80.00% and 63.33%) groups. However, less than 10% common mutations were found in both CSCLC and pure SCLC. When analyzing the data of SCLC and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) components of CSCLC, more than 50% common mutations, and identical genes with mutations were detected. Moreover, there were also common biological processes and signaling pathways identified in CSCLC and pure SCLC, in addition to SCLC and NSCLC components.
Conclusions: There were no significant differences in terms of clinical features between CSCLC and pure SCLC. However, the prognosis for CSCLC was worse than pure SCLC. NGS analysis suggested that CSCLC components might derive from the same pluripotent single clone with common initial molecular alterations and subsequent acquisitions of other genetic mutations.
Keywords: Combined small cell lung cancer (CSCLC); comprehensive genomic profiling; small cell lung cancer (SCLC); targeted gene sequencing.
2021 Translational Lung Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037tlcr-20-1099). Dr. JM serves as an unpaid editorial board member of Translational Lung Cancer Research from Aug 2019 to Aug 2021. The authors have no other conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
